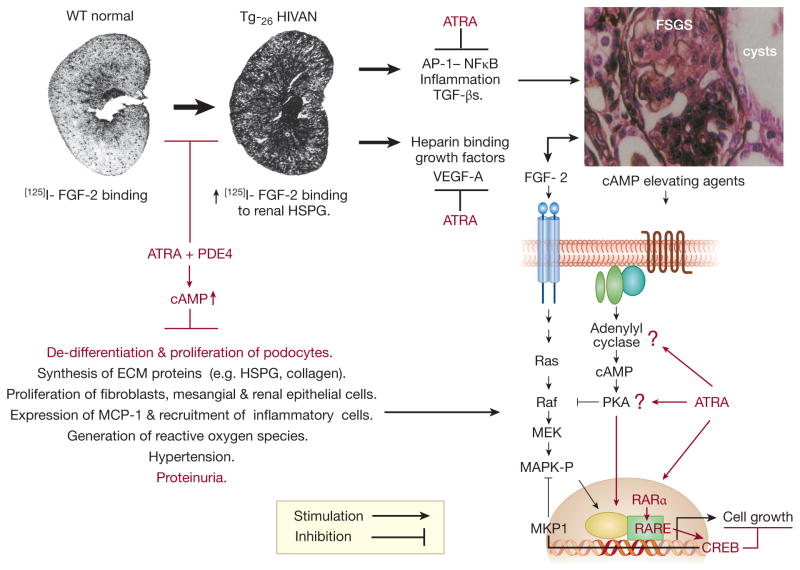
Figure 1. A summary of the possible roles that all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) and Roflumilast (PDE4) may have to prevent the progression of HIVAN in HIV-Tg26 mice.
Zhong et al.1 showed that ATRA + PDE4 prevented the progression of HIVAN in Tg mice by blocking the de-differentiation and proliferation of podocytes through a cAMP/PKA/CREB dependent mechanisms that is independent of HIV-1 genes (highlighted in red color). Based on the pathogenesis of the renal disease in Tg26 mice3–5, and the known beneficial effects of these drugs in other experimental models of renal diseases 6–8, we have highlight additional pathological pathways (black color) that might be affected as well. Abbreviations: ATRA = all-trans retinoic acid analogs; PDE4 = cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor; cAMP = cyclic adenosine monophosphate; FGF-2 = Fibroblast Growth Factor-2; HSGP = heparan sulfate proteoglycans; ECM = extracelllular matrix proteins; MCP-1 = Monocyte Chemoattractant Protein 1; AP-1= Activator Protein-1; NFkB = Nuclear Factor Kappa B; TGF-β = Transforming Growth Factor Beta; VEGF-A = Vascular Endothelial Cell Growth Factor-A; FSGS= Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis; Ras = rat sarcoma G protein; Raf = rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma protein kinase; MEK = mitogen activated protein kinase / Erk kinase; MAPK-P = mitogen-activated protein kinase - phosphorylated / ERK-P; MKP-1 = mitogen activated protein kinase phosphatase-1; PKA = protein kinase A; RAR α = retinoic acid receptor alpha; RARE = retinoid acid responsive element; CREB = cAMP responsive element binding protein.