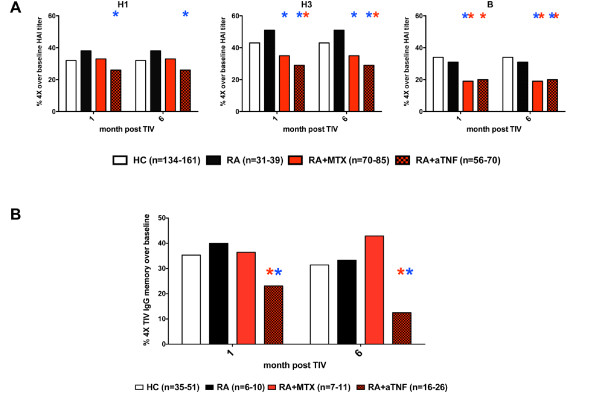
Figure 2.
Induction of serum antibodies and memory B cells. (a) The frequency of subjects within each group that had a four-fold or greater increase in serum hemagglutination inhibition assay (HAI) titer over baseline was determined in 2006/2007 through 2009/2010 influenza seasons, and combined results indicated. (b) Total B cells were isolated, cultured with CpG and IL-2 for four days, and trivalent influenza vaccine (TIV) and total IgG specific EliSpots performed to determine the frequency of TIV-specific memory B cells. The frequency of subjects that had a four-fold or greater increase in the frequency of TIV-specific IgG memory B cells over baseline is presented. The red star indicates significant difference (P < 0.05) compared with healthy control (HC) group, the blue star indicates significant difference as compared with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) group. An individual subject may have provided data from multiple study years. N, the cumulative number of paired subject events measured throughout the multiple years.