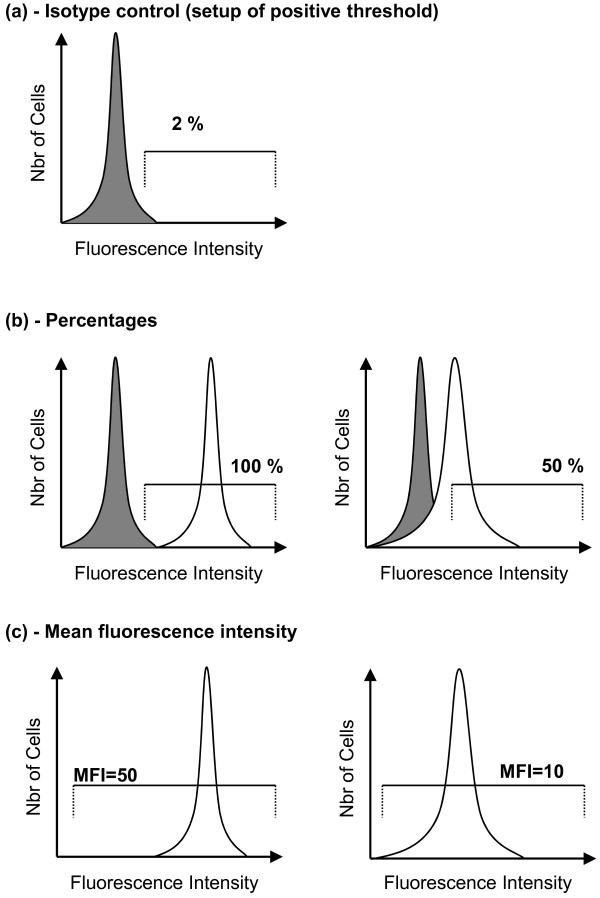
Figure 3.
Measurement of percentage or mean fluorescence intensity by flow cytometry (theoretical histograms). (a) Isotype control (gray peak), a nonrelevant immunoglobulin labeled with similar fluorochrome as the staining antibody. This identifies nonspecific staining and enables one to set up a region of positive/specific staining (usually set up between 1 and 2%). (b) Percentages. After setting up the region of positive staining using isotype control, staining with specific antibody is acquired. In healthy volunteers (left histogram) about 100% of circulating monocytes express HLA-DR, whereas in septic shock patients (right histogram) this percentage is decreased. (c) Mean fluorescence intensity (MFI). The average intensity of fluorescence on all cells of interest is measured. In cases of circulating monocyte human leukocyte antigen-DR expression (mHLA-DR) measurements, the gated region includes all monocytes and the MFI value is decreased in septic patients (right histogram) in comparison with the normal value (left histogram). However, the measurement of this parameter is highly dependent on the flow cytometer settings and cannot be compared between two laboratories. To circumvent this, kits using calibrated beads and calculating the number of antibodies bound per cells (AB/C) have been developed. Regarding mHLA-DR expression, the usual threshold of 30% positive monocytes (retained in several studies for predicting mortality after sepsis) is similar to 5,000 AB/C [20].