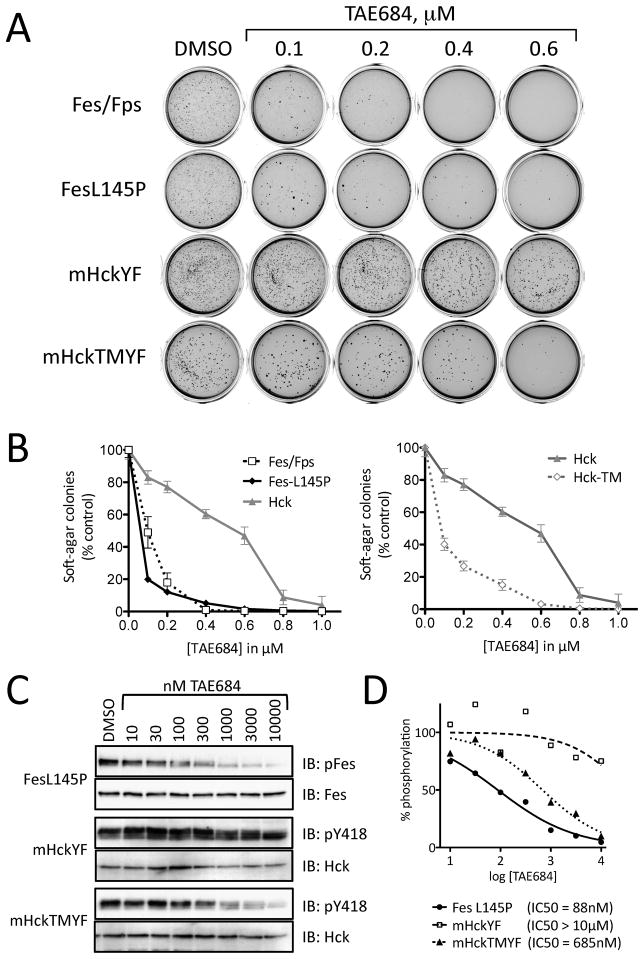
Figure 5. Inhibition of soft-agar colony formation by rodent fibroblasts transfected with transforming variants of c-Fes.
Rat-2 fibroblasts were transformed with a constitutively active c-Fes-L145P coiled-coil mutant, a c-Fes/v-Fps chimeric kinase, a tail-activated mutant of the Src-family kinase Hck (Hck-YF) or the active Hck mutant plus a T338M gatekeeper mutation (Hck-TMYF). Fibroblast transformation was determined in a soft-agar colony formation assay in the presence of 0.1% DMSO (control) and increasing concentrations of TAE684 as shown. A) Scanned images of representative plates showing stained soft-agar colonies. B) The number of transformed colonies was determined from the scanned images using Quantity One® software (BioRad). Soft-agar colony growth is expressed as the mean percent of colonies observed relative to the untreated control in triplicate assays ± SD. C) Transformed Rat-2 cells were grown in monolayer culture and treated with the indicated concentrations of TAE684 for 16 h. Cell lysates were prepared and autophosphorylation of the transforming kinases were assessed by immunoblotting with phosphopspecific antibodies. D) The data shown in C were quantified and IC50 values were determined by curve fitting. See also Figure S5.