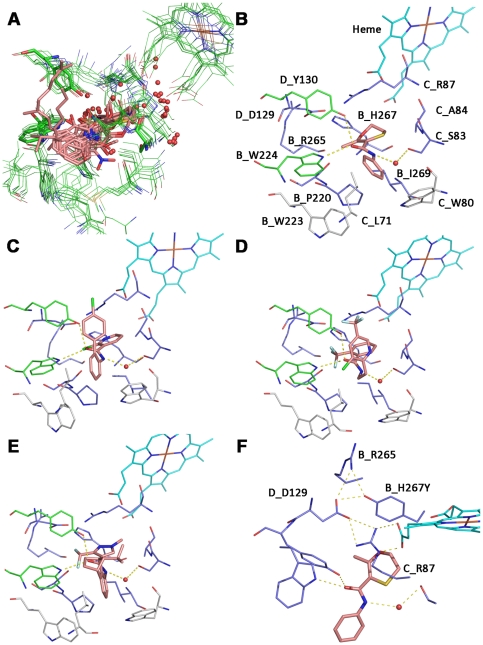
Figure 3. Tridimensional model of the M. graminicola SDH with Qp site docked carboxamides and interactions to substituted residues.
A: Superposition of all complex II crystal structures with a resolution higher than 3 Å. Only amino acids that are in a 5 Å radius to the bound ligands in the quinone binding site are shown. Amino acids and the heme are represented in lines, the ligands in sticks and water molecules as non bonded spheres. The color code is presented according to atom types. Amino acid and heme carbons are colored in green, ligands carbons in salmon. B: putative binding mode of carboxin in a tridimensional model of M.graminicola SDH. The heme carbons are represented in cyan sticks, the carboxin carbon atoms in salmon. Amino acids that are involved in resistance after mutation are colored in dark blue, amino acids that make key interactions are shown in green and amino acids that are in close proximity to the ligand but which were not found substituted in this study are colored in grey. Hydrogen bonds are shown as yellow dotted lines. C: Putative binding mode of Boscalid in M.graminicola SDH. D: Putative binding mode of Fluopyram in M. graminicola SDH. E: Putative binding mode of Isopyrazam in M. graminicola SDH. F: Model of M. graminicola SDH where SDHB histidine 267 is mutated into a tyrosine. The putative binding mode of the mutated enzyme with Carboxin is shown.