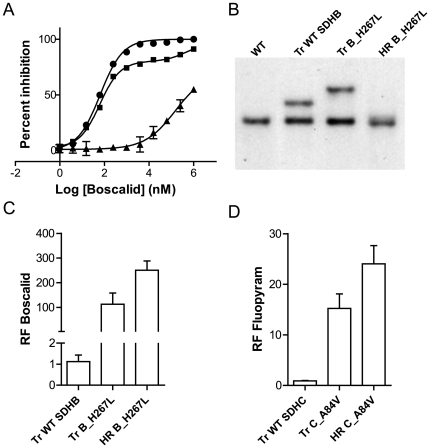
Figure 5. Comparison of the resistance phenotypes displayed by transformants of the SDHB or SDHC subunits.
Two types of transformants were created, (i) Tr strains where the genes encoding either SDHB or SDHC subunits were ectopically inserted under the control of a GPDA promoter, (ii) HR strains where the WT gene was replaced by a mutated version in its original genomic context. A: SDH inhibition displayed by mitochondrial extracts as measured with the succinate: Q0/DCPIP reduction test in the presence of varying concentrations of Boscalid. Fitted curve is monophasic with the ectopic transformant containing the WT SDHB expression cassette (black dots) and with the homologous recombinant strain carrying the SDHB_H267L mutation (HR B_H267L, black triangles). Inhibition is biphasic with the ectopic transformant containing the SDHB_H267L expression cassette (Tr B_H267L, black squares). B: Southern blot of genomic DNA extracted from (left to right), the WT (IPO323), one ectopic transformant carrying the WT_SDHB expression cassette, one ectopic transformant carrying the SDHB_H267L expression cassette and signal obtained with one SDHB_H267L homologous recombinant. Boscalid (C) and Fluopyram (D) resistance phenotypes displayed by ectopic and homologous recombinants transformants. In both cases when additional WT SDHB (Tr_WT_SDHB) and SDHC (Tr_WT_SDHC) were inserted ectopically, no significant increase in resistance was observed. When an additional mutated copy of SDHB (Tr_SDHB_H267L) or of SDHC (Tr_SDHC_A84V) was inserted ectopically, significant resistance to the compounds was observed, clearly indicating a dominant effect of the mutated alleles. However, in the homologous recombinant strains where only the mutated subunit SDHB (HR_SDHB_H267L) or SDHC (HR_SDHC_A84_V) was present a further increase in resistance is observed. Whiskers represent minimum and maximum RFs obtained, boxes represent 95% confidence interval and bars value of the median. The data presented correspond to average values of duplicated tests with four independent events of each kind.