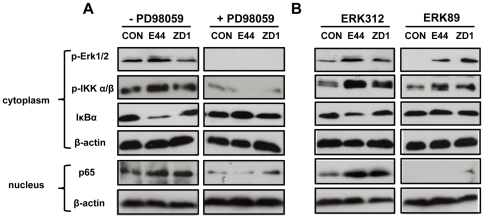
Figure 2. Inhibition of IbeA+ E. coli-induced IKK phosphorylation and NF-κB activation by MEK/ERK inhibitors.
(A) HBMECs were incubated with or without PD098059 (50 µM) for 60 min before stimulation with E44 or ZD1 (107/ml). (B) HBMECs were incubated with or without ERK89 (vimentin-binding domain, 25 µg/ml) and ERK312 (control peptide, 25 µg/ml) for 60 min before infection with E44 or ZD1 (107/ml). In both (A) and (B), ERK1/2 phosphorylation (p-Erk1/2), IKK α/β phosphorylation (p-IKK α/β) and IκBα degradation were examined in cytoplasmic fractions after 30 min of stimulation with E. coli K1 strains. NF-κB (p65) translocation to the nucleus was examined in nuclear fractions after 2 h of infection with E. coli K1 strains. β-actin in both fractions was detected as internal loading controls. CON, control without bacterial stimulation.