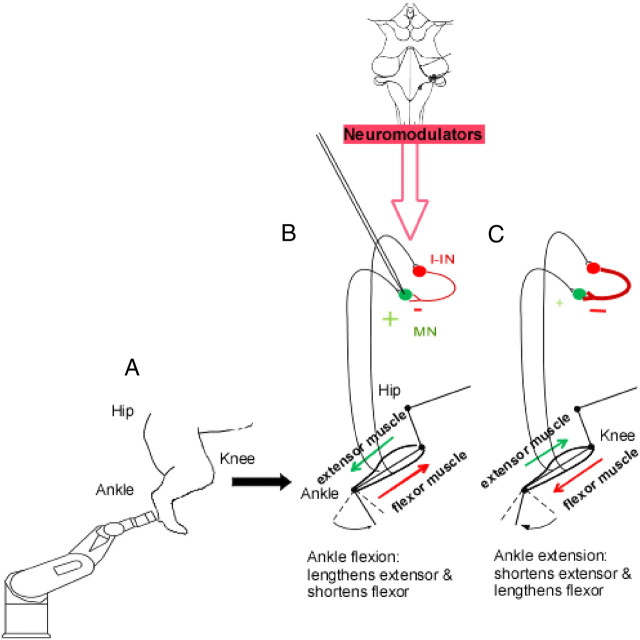
Figure 1.
A, A robotic arm attached to the cat's foot flexed and extended the ankle joint. B, With the system intact, as shown here, ankle flexion stretches extensor muscles and provides monosynaptic excitation that depolarizes the extensor MN; at the same time, the flexor muscles are shortening, decreasing the amount of inhibition from inhibitory interneurons (I-IN). C, During extension, the opposite occurs: inhibition to the MN increases while excitation decreases.