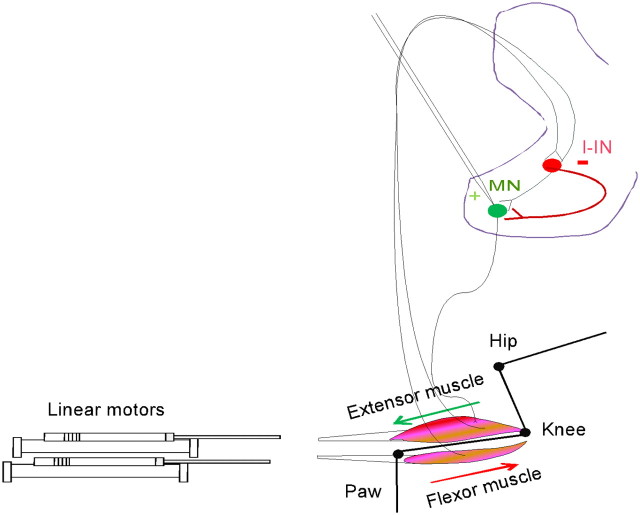
Figure 4.
Illustration of the computer-controlled linear motor set up to test the push–pull hypothesis within cells. The distal tendons to ankle extensor and flexor muscles were attached to the linear motors, which independently controlled muscle lengths while measuring effective synaptic currents in ankle extensor motoneurons. I-IN, Inhibition from inhibitory interneurons.