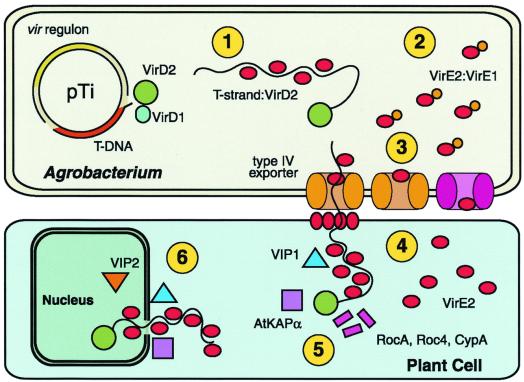
Figure 1.
The six functions of VirE2. The vir regulon, encoding the major loci virA-E and virG-H, is expressed on detection of plant wound signals. VirD2 and VirD1 liberate the T-strand and VirD2 remains covalently bound to the 5′ end. 1: VirE2 coats the T-strand, protects it from degradation, and maintains it in a transportable conformation. 2: VirE2 associates with VirE1, required for VirE2 export. 3: VirE2 exits Agrobacterium via the type IV exporter independently, or as part of the T-complex. Alternatively, VirE2 may exit by an alternate pathway (pink; ref. 4). 4: VirE2 forms a pore in the plant plasma membrane allowing passage of the T-complex and coats the T-strand in the plant cytoplasm. 5: VirD2 and VirE2 interact with plant cytoplasmic chaperones (RocA, Roc4, and CypA). Other factors (AtKAPα, VIP1) may target the T-complex to the nucleus. 6: VirE2 interacts with nuclear factors (VIP2) that mediate interaction with chromatin and facilitate integration of the T-strand.