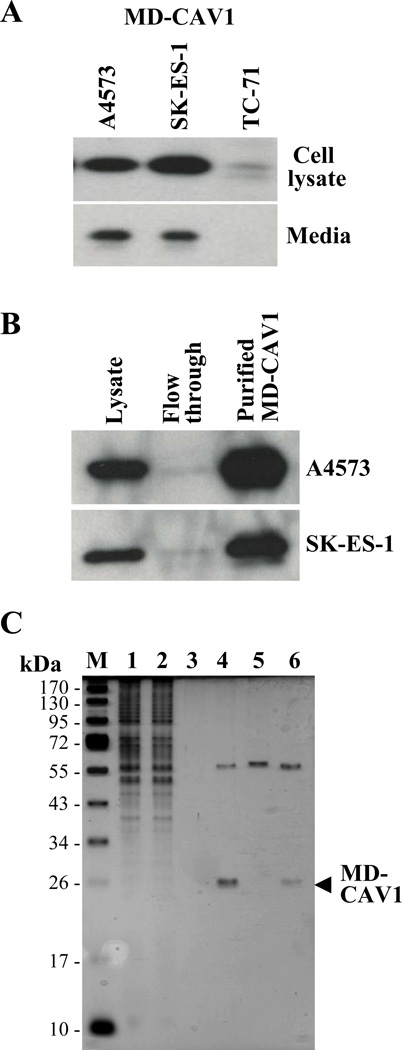
Figure 3. Ectopically expressed human CAV1 is secreted and taken up by EWS cells.
(A) The Myc-DDK-tagged (MD-CAV1) protein was detected using anti-Myc antibodies in cell lysates (upper panel) and conditioned media (lower panel) prepared from the indicated EWS cells stably transfected with Myc-DDK-CAV1. (B) The MD-CAV1 protein was purified from A4573 (upper panel) and SK-ES-1 cells (lower panel) using anti-FLAG magnetic beads; samples of the cell lysates, flow through and the eluted fractions were resolved by SDS-PAGE and subjected to immunodetection with anti-Myc antibodies. (C) Purification of MD-CAV1. MD-CAV1 was purified using anti-FLAG magnetic beads as described under “Materials and methods”. Samples from the various steps of the purification process were resolved by SDS-PAGE, and the purity of the protein was assessed using silver staining. M, denotes marker, while lanes correspond to the following: (1) cell lysate – 3 µl; (2) flow through following incubation with anti-FLAG beads – 3 µl; (3) TBS washing of the beads – 3 µl; (4) bound protein eluted with glycine HCl – 10 µl ; (5) magnetic beads alone treated with glycine HCl – 10 µl; and (6) bound protein eluted with Laemmli buffer – 10 µl.