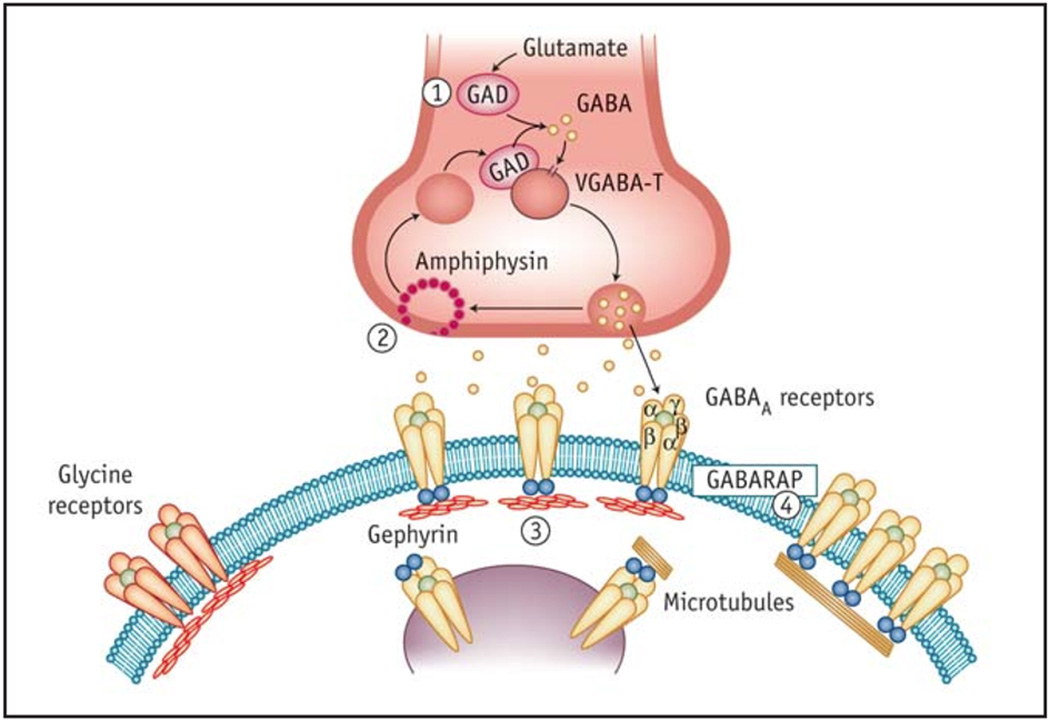
Figure 3.
Components of the inhibitory synapse recognized by known antibodies in Stiff Person Syndrome. The pre-synaptic glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) (1) is the rate-limiting enzyme in GABA synthesis; amphiphysin (2) is a cytosolic, pre-synaptic vesicle-associated protein responsible for endocytosis of vesicle plasma membranes following GABA release. The post-synaptic target antigens in SPS are gephyrin (3), and GABA-A-receptor-associated protein (GABARAP) (4). Gephyrin is a cytosolic, tubulin-binding protein involved in clustering the glycine and GABA-A receptors in the spinal cord and the brain. GABARAP is a linker protein between gephyrin and GABA-A receptors and promotes recycling and organization of the GABA receptors. The most common autoantigen in SPS is GAD, which is seen in 85 % of patients, followed by GABARAP, which is found in 65 % of patients. Amphiphysin is detected in 5 % of patients, while gephyrin has been seen only in one case. (From reference 91 with permission).