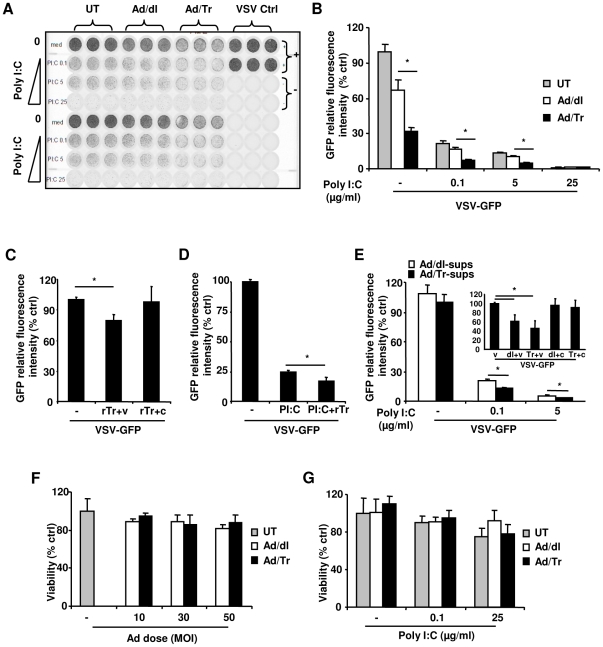
Figure 2. Tr/E significantly reduce VSV-GFP infection and enhance polyI∶C-driven antiviral protection in Ad/Tr-cells.
Untreated (UT) or treated with MOI 50 of Ad/dl or Ad/Tr HEC-1A cells were medium- or polyI∶C 0.1–25 µg/ml-treated for 24 h, followed by MOI 1 VSV-GFP. GFP fluorescence intensity was visualized 24 h later using a Typhoon scanner (A), and relative fluorescence intensity to virus positive control was determined and presented as % of UT control (B). (C) VSV-GFP load after pre-incubation of 5 µg/ml of rTr either with MOI 1 of VSV-GFP (rTr+v) or cells (rTr+c) for 1 h, followed by their washing and addition of VSV-GFP. Medium-treated VSV-GFP (v) served as a positive control. (D) HEC-1A cells were treated with 5 µg/ml of rTr for 1 h in serum-free medium, after which medium or 0.1 µg/ml polyI∶C was added for 24 h followed by MOI 1 of VSV-GFP. This polyI∶C dose was chosen because anti-inflammatory effects of secreted/soluble proteins, compared to Ad/Tr-cells, were less potent. (E) HEC-1A cells were pretreated with equal volumes of supernatants from Ad/dl-cells (Ad/dl-sups) and Ad/Tr-cells (Ad/Tr-sups, 5 µg/ml final concentration) for 1 h before medium or 0.1 or 5 µg/ml polyI∶C was added for 24 h followed by MOI 1 VSV-GFP. Lower polyI∶C doses were used to better visualize VSV-GFP viral replication 24 h later, using a Typhoon scanner. Insert in panel (E) depicts VSV-GFP load after pre-incubation of same volumes and concentrations of Ad/dl- and Ad/Tr-sups with either MOI 1 VSV-GFP (dl+v) or (Tr+v), respectively, or cells (dl+c) or (Tr+c) for 1 h, followed by washing and addition of MOI 1 VSV-GFP. Medium-treated VSV-GFP (v) served as an untreated control. The data are representative of at least two independent experiments performed in triplicate and shown as mean ± SD. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA or Student's t test in (C), and * representing significant difference, when p<0.05. (F and G) Cell growth and metabolic activity of HEC-1A cells were determined by standard MTT Cell Viability Assay Kit following infection with MOI 10–50 of Ad/dl or Ad/Tr (F) or after stimulation with increasing doses of polyI∶C (G). Cell viability was expressed as % of untreated cells, which served as a negative control group, and was designated 100%; the results are expressed as % of negative control.