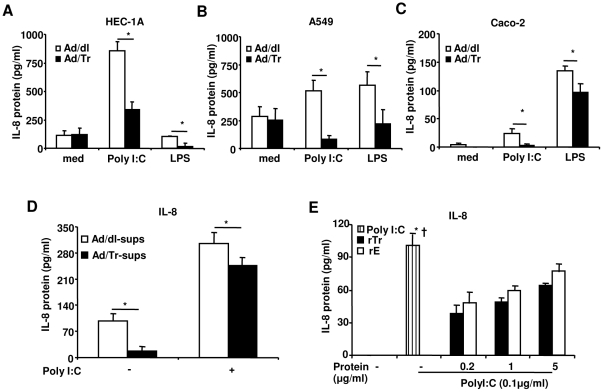
Figure 8. Tr/E significantly reduce protein secretion of IL-8 in ECs following polyI∶C and LPS stimulation.
Secretion of IL-8 in supernatants from HEC-1A (A), A549 (B), and Caco-2 (C) cells initially infected with MOI 50 of Ad/dl or Ad/Tr and subsequently stimulated with either 25 µg/ml of polyI∶C or 1 µg/ml of LPS for 24 h. Following stimulation, supernatants were tested for IL-8 secretion by ELISA. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments performed in triplicate and expressed as the mean ± SD, shown in pg/ml. Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t test with * representing significant difference between the groups, p<0.05. (D) Secretion of IL-8 in supernatants from HEC-1A cells that were pre-treated with HEC-Ad/dl and HEC-Ad/Tr supernatants before polyI∶C stimulation. HEC-1A received 50 µl of concentrated supernatants containing around 10 µg/ml of Tr/E in Ad/Tr supernatants and 0.004 µg/ml of Tr/E in Ad/dl sups for 1 h, to which additional 50 µl of medium alone or polyI∶C to the final concentration of 0.1 µg/ml were added for 24 h. (E) Secretion of IL-8 in supernatants from HEC-1A cells treated with commercial 6×His-Tr (rTr) or in-house HAT-E (rE) for 1 h and then stimulated with medium alone or 0.1 µg/ml of polyI∶C for 24 h. A lower dose of polyI∶C was used in (D) and (E), since anti-inflammatory effects of secreted/soluble proteins, compared to Ad/Tr-cells, were less potent. Statistical analysis was performed using ANOVA, and * representing significant difference between the polyI∶C group and rTr groups; † representing significant difference between the polyI∶C and rE groups, p<0.05.