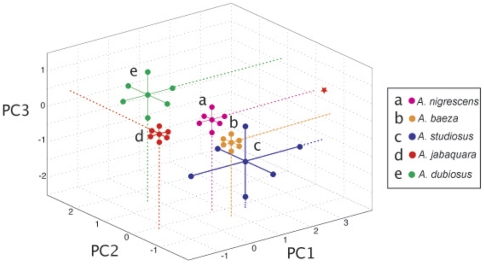
Figure 3. Three of the five species investigated show significant differences in their mean position along three principal component axes.
The 95% confidence intervals for each species show moderate overlap between Anelosimus studiosus with A. baeza and A. nigrescens, but this may be due to the small sample size of A. studiosus. The social and intermediate social species (A. dubiosus and A. jabaquara) segregate from the subsocial and nearly solitary species (A. studiosus, A. baeza and A. nigrescens) along the first PC axis, which correlates with the distance from the forest edge (more negative values indicate that nests occur further inside the forest). Along the second PC axis, A. dubiosus differs from the other four species; more positive values indicate nests that are closer to the ground and built on the core of the plant. The three subsocial and nearly solitary species differ along the third PC axis, which reflects the local nest position and instar. The star represents the point where the confidence intervals measuring the position of Anelosimus jabaquara intercepts the y and z axis.