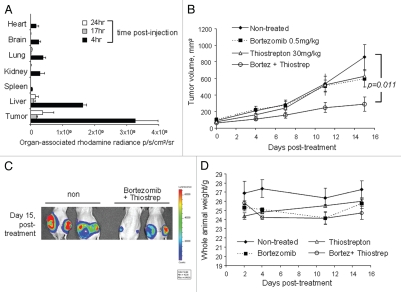
Figure 1.
Effect of bortezomib and micelle-thiostrepton treatment on MDA-MB-231-luc tumor xenograft models. (A) Biodistribution of rhodamine-labeled micelle-thiostrepton complexes in tumor-bearing mice. High micelle-associated fluorescence is apparent in tumors and in the liver 4 h post-injection. Value for each organ represents an average of n = 2–4. (B) Anticancer effects of bortezomib (0.5 mg/kg) alone, micelle-thiostrepton treatment (30 mg/kg) alone, a combination of bortezomib and micelle-thiostrepton on MDA-MB-231 xenograft volumes, after five treatments over 15 d, n = 6–8. All averages were considered significant, and the t-test p value of the non-treated and the V+T-treated tumors was calculated to be 0.011. Error bars represent SEM. (C) Change in tumor-associated bioluminescence in animals bearing breast cancer xenografts after continuous treatment with a combination of complementary proteasome inhibitors over 15 d. Luciferase expression demonstrates that the sizes of tumors treated with bortezomib and thiostrepton were much smaller in size than the non-treated controls. (D) Change in animal weight during treatment schedule. Only the animals receiving the combination of proteasome inhibitors demonstrated slight weight loss, compared with non-treated and single drug-treated animals.