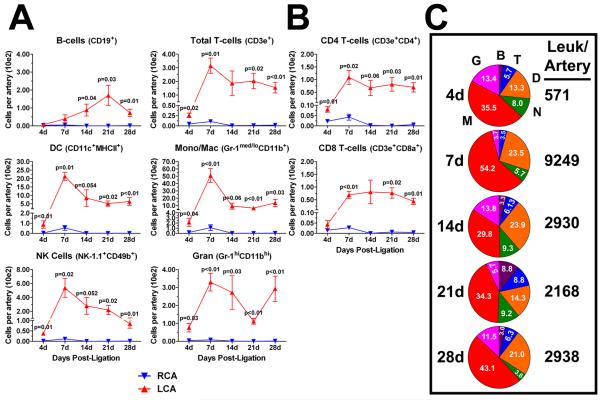
Figure 3. Disturbed flow induces a transient peak accumulation of innate cells, sustained T-cell accumulation, and delayed B-cell entry into LCA.
The flow cytometry data shown in Figure 2a was further analyzed to quantitate dynamic changes in specific immune cell lineages. A, Leukocytes (CD45+) were subdivided into six major immune cell types (B- and T-cells, DCs, monocyte/macrophage, NK cells and granulocytes) over a four week time course in LCA and RCA. B, T-cells were further subdivided into CD4 and CD8 T-cells. Shown (A-B) are absolute cell numbers (in hundreds) per carotid artery (n=4 to 5 pools of 3 arteries each). C, Pie charts show compositional analyses of vascular leukocytes in the flow-disturbed LCA, presented in (A). Each pie slice denotes mean percentage of total leukocytes (white numbers). Numbers to the right of the pie charts denote mean leukocyte numbers per carotid artery. Data are mean values ±SEM. B, B-cells; T, T-cells; D, DCs; N, NK-cells; M, macrophages; G, granulocytes.