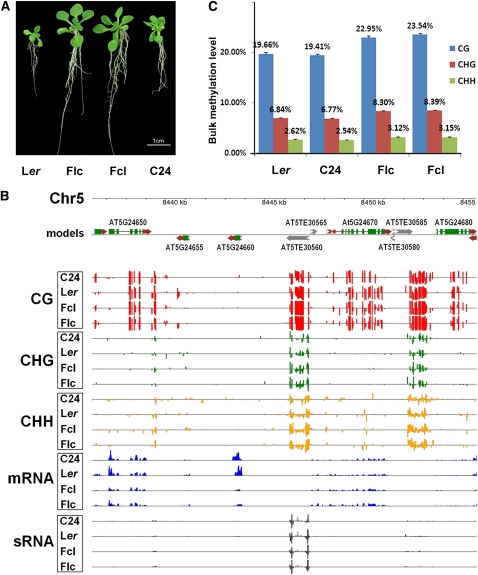
Figure 1.
DNA Methylation Landscapes of the Genomes of Ler and C24 and Their Reciprocal Hybrids.
(A) Heterotic phenotypes of 15-d-old Arabidopsis F1 hybrids relative to their parents. Flc, F1 where maternal line is Ler; Fcl, F1 where maternal line is C24.
(B) An example of DNA methylation profiles at three cytosine contexts and correlated mRNA and sRNA profiles in a representative region of chromosome 5 in Arabidopsis F1 hybrids and their parents. The top panel shows annotated protein-coding genes and TEs in this region based on the TAIR10 release of the Arabidopsis genome. Predicted coding sequences are shown in green, 5′- and 3′-untranslated regions are shown in red, and predicted TEs are shown in black. The directions of both genes and TEs are indicated by arrows. The bottom panel shows the locations of cytosine methylation, mRNAs, and sRNAs detected by high-throughput sequencing. The height of the bar is proportional to the number of reads detected on each strand.
(C) Elevated DNA methylation in F1 hybrids relative to their parents. Columns represent bulk methylation levels at three cytosine contexts in the parental and hybrid genomes as determined by bisulfite sequencing. Data are averages of three independent biological replicates, each consisting of 100 pooled seedlings of the corresponding genotype. Error bars represent sd.