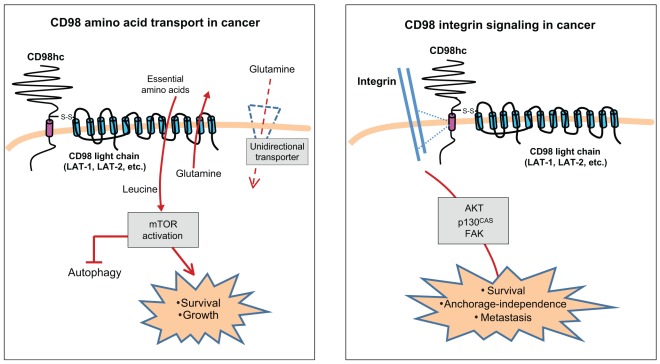
Fig. 4.
Roles of CD98 in cancer. CD98 has two main biochemical functions, amino acid transport and integrin signaling; both appear important in tumor growth and metastasis. Left panel: CD98 amino acid transport in cancer. LAT-1 and LAT-2, the most commonly studied CD98 light chains, are system L bi-directional transporters of large neutral amino acids. Unidirectional transporters (such as system A or N transporters) import the non-essential amino acid glutamine into a rapidly growing cell. LAT-1 or LAT-2 can then export glutamine in exchange for importing EAAs. EAAs then activate the mTOR pathway, blocking autophagy and promoting cell growth and protein synthesis. Right panel: CD98 integrin signaling in cancer. CD98hc interacts with integrins and mediates integrin-dependent signals that promote tumorigenesis. CD98-dependent integrin signaling through proteins such as AKT, p130CAS (also known as BCAR1) and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) allow tumor cell survival and proliferation without anchorage.