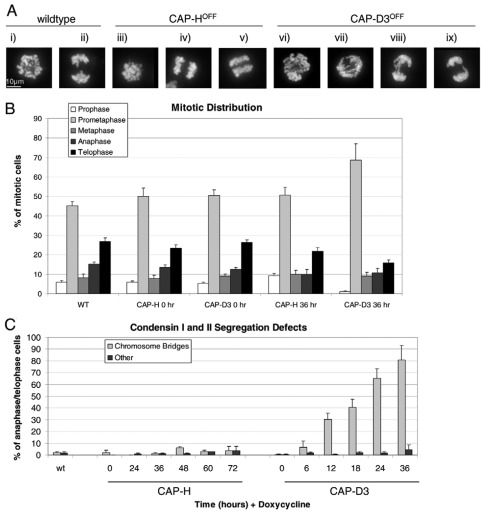
Fig. 3.
Mitotic stage analysis and chromosome segregation defects. (A) PFA-fixed cells stained with DAPI showing metaphase (i, iii and vi) and anaphase cells (ii, iv, v and vii–ix), revealing the presence of chromosome-segregation defects mainly in CAP-D3 knockout (KO) cell lines (vii–ix). (B) Mitotic-stage analysis of wild-type (WT), CAP-H and CAP-D3 KO cell lines, with and without doxycycline at 0 and 36 hours (see supplementary material Fig. S3 for a more detailed time-course distribution). PFA-fixed mitotic cells were stained with DAPI and probed with antibodies against phosphoserine 10 histone H3and lamin B1 or INCENP and β-tubulin as cell cycle markers. (C) Chromosome-segregation defect analysis in CAP-H and CAP-D3 KO cell lines. The major chromosome-segregation defects visible under PFA fixation and DAPI staining were divided into two categories and scored as a percentage of total anaphase and telophase cells: chromosome bridges and ‘other’ (defined as anaphases with lagging chromosomes or multipolar anaphases with chromosomes separating to more than two spindle poles). Error bars represent the standard error.