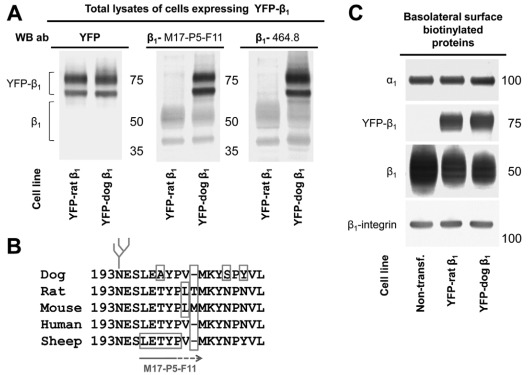
Fig. 1.
The monoclonal antibodies raised against the rabbit or sheep β1 subunit react with YFP–dog-β1 but not with YFP–rat-β1. (A) Western blot analysis of total lysates of MDCK cells expressing either YFP–dog-β1 or YFP–rat-β1 using antibodies against YFP and two types of monoclonal antibodies to β1. Both 464.8 and M17-P5-F11 anti-β1 antibodies, raised against rabbit and sheep subunits, respectively, react with the endogenous β1 subunit and YFP–dog-β1 but do not react with YFP–rat-β1. Antibodies to YFP react both with YFP–dog-β1 and with YFP–rat-β1. (B) Multi-species sequence alignment of the region containing the epitope of M17-P5-F11 antibody as deduced from screening a bacteriophage epitope library (Sun and Ball, 1994). The epitope of the 464.1 antibody is unknown. (C) Western blot of proteins isolated by basolateral surface-selective biotinylation showing the presence of both rat and YFP–dog-β1 fusion proteins in the basolateral membranes. Expression of either YFP–dog-β1 or YFP–rat-β1 in MDCK cells resulted in a substantial decrease in the amount of the endogenous Na+/K+-ATPase β1 subunits in the basolateral membranes but did not change the level of the α1 subunits in comparison with that of non-transfected (‘Non-transf.’) cells. β1-integrin was used as a loading control.