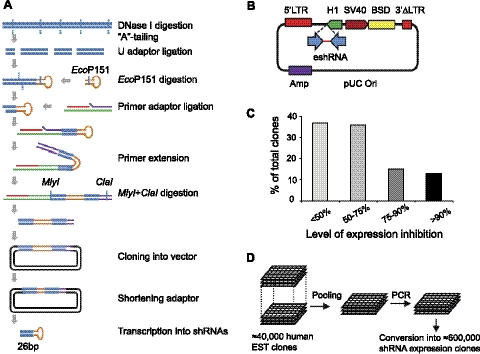
Figure 1.
Development of an EST-derived 26-nt shRNA library. A) Schematic outline of the enzymatic procedure to convert double-stranded DNA fragments into structures expressing 26-nt shRNAs. Details are given in Materials and Methods. B) Lentiviral shRNA-expressing vector pLentiSuper2. 5′LTR, 5′ long terminal repeat; 3′ΔLTR, promoter-deleted 3′ long terminal repeat; H1, RNA polymerase III H1 promoter; SV40, SV40 viral prompter; BSD, blasticidin selection marker; eshRNA, enzymatic prepared shRNA; Amp, ampicillin selection marker. C) Knockdown efficiency of shRNAs from a single gene library. HEK293T cells were cotransfected with 800 ng DNA of 60 individual shRNA-expressing clones or empty vector pLentiSuper2, together with 200 ng DNA of target gene (ARRDC1-GFP) and 50 ng DNA of nontarget control. Expression of both target and control genes were detected by immunoblotting using an anti-GFP antibody. Expression level of ARRDC1-GFP was normalized to that of GFP. Knockdown efficiency by shRNA was calculated as percentage relative to empty vector controls. D) Pooling and conversion of a large collection of ESTs into the shRNA library.