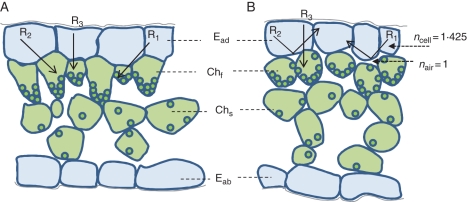
Fig. 7.
Diagrammatic explanation of structural variegation due to intercellular spaces above the chlorenchyma. A change in refractive index occurs at the interface of air spaces and plant cells due to the intercellular spaces above the funnel-shaped chlorenchyma. In the green area (A), incident light at various angles is transmitted between epidermal cells and adjacent chlorenchyma without reflection at the interface. In contrast (B), when the incident light travels obliquely at angles >44·6° to the normal at the interface between a plant cell and an air space, it is completely reflected at the boundary of the cell wall (R1 and R2). Thus, the leaf colour of this area appears lighter. Note also that the funnel-shaped chlorenchyma cells in light areas (B) are more or less isodiametric, with chloroplasts not so strictly confined to the tapering base of the cell as in green areas (A). Abbreviations: Eab, abaxial epidermis; Ead, adaxial epidermis; Chf, funnel-shaped chlorenchyma; Chs, spongy chlorenchyma.