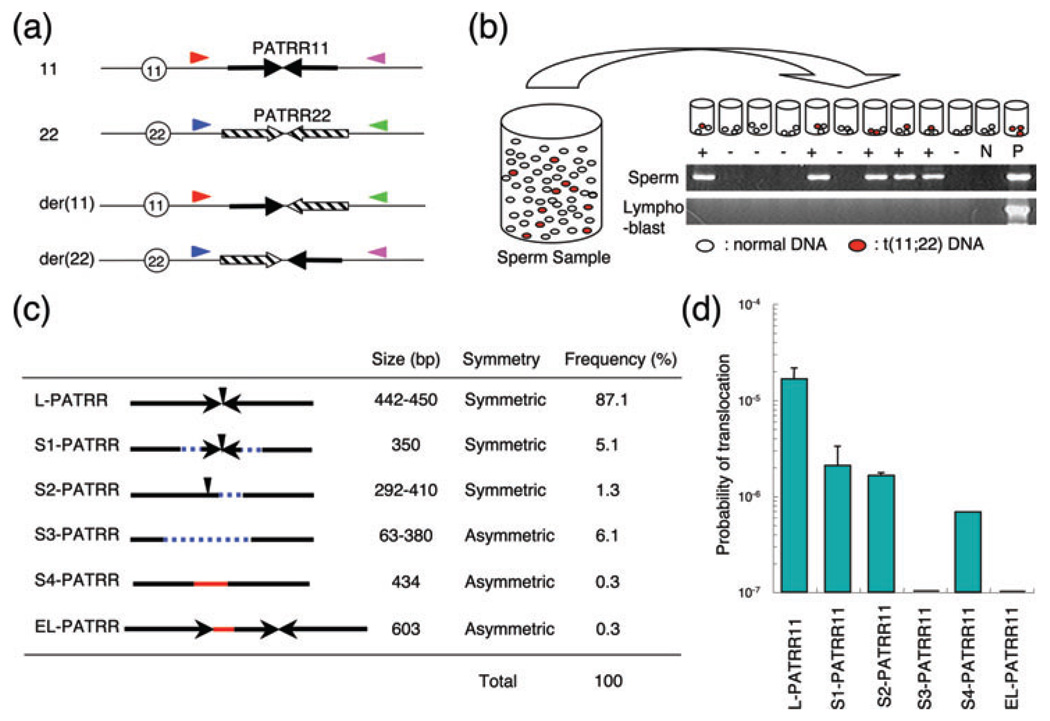
Fig. 2.
Polymorphisms of the palindrome affect the de novo translocation frequency. (a) Location of PCR primers. Arrows indicate each arm of the PATRR11 (solid arrows) and PATRR22 (hatched arrows). Size polymorphisms of the PATRR11 were examined by PCR using primers indicated by red and pink triangles. Translocations were detected using one of the primers flanking the PATRR11 (red or pink triangles) and with one of the primers flanking the PATRR22 (blue or green triangles). Centromeres are represented by circles. (b) Strategy for estimation of translocation frequency by PCR. Genomic DNA was extracted from sperm samples. Translocation-specific PCR was performed using multiple batches of template DNA. The translocation frequency was calculated using the equation, q = 1 − (1 − p)1/n; with n = number of haploid genomes per aliquot, p = the probability that an aliquot contains a translocation, product and q = the probability that one randomly selected haploid genome in a given aliquot sustained a translocation. The gel images show representative PCR results. The upper panel shows results derived from sperm DNA, whereas the lower panel presents results from lymphoblast DNA. Lane M, size marker; lane N, negative control; lane P, genomic DNA from a t(11;22) balanced carrier serving as a positive control. (c) Characterization of the PATRR11 variants. Arrows indicate each unit of inverted repeats. Vertical arrowheads indicate the center of the palindromic sequence. Dotted blue lines show the deleted region, while red lines indicate the insertion of sequences of unknown origin. Other characteristics and the frequency in the general population are shown on the right. (d) A histogram showing the probability of de novo translocation by allele types. Each bar represents the mean value and the vertical bar indicates standard deviation on a log scale. The allele types are abbreviated. PCR, polymerase chain reaction; PATRR, palindromic AT-rich repeat.