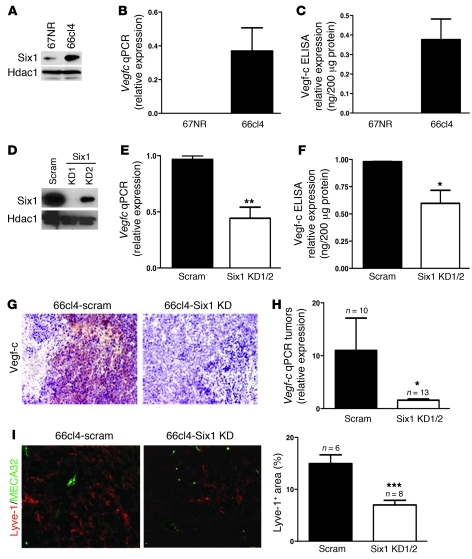
Figure 4. Knockdown of Six1 in 66cl4 mammary carcinoma cells leads to a reduction in Vegf-c and lymphangiogenesis.
(A) Western blot analysis demonstrates increased Six1 expression in the metastatic 66cl4 cell line as compared with that in the syngeneic, nonmetastatic 67NR cell line. (B) Real-time PCR demonstrates that Vegfc mRNA is increased in 66cl4 cells as compared with that in 67NR cells. (C) 66cl4 cells contain high levels of Vegf-c in their conditioned media, as assessed by ELISA. (D) Expression of Six1 in 66cl4 cells expressing either a control (scram) or Six1 knockdown (KD1/KD2) construct. Two shRNAs were used to knockdown Six1 and are individually shown in the panel while shown as Six1 KD1 and Six1 KD2 in the following panels. (E) Vegfc mRNA is decreased in 66cl4-Six1 KD cells relative to that in 66cl4-scramble cells, as measured by real-time PCR. (F) Vegf-c protein is decreased in the conditioned media from 66cl4-Six1 KD cells relative to that in 66cl4-scramble cells, as measured by ELISA. (G) 66cl4-Six1 KD tumors express less Vegf-c, as detected by immunostaining, than 66cl4-scramble (66cl4 scramble) control tumors. Representative images are shown. Original magnification, ×200. (H) Real-time PCR demonstrates that 66cl4-Six1 KD tumors contain less Vegfc mRNA than the 66cl4-scramble control tumors. (I) 66cl4-scramble and Six1 KD tumors were stained with antibodies against Lyve-1 (red) and MECA32 (green), and representative images are shown. Original magnification, ×400. SlideBook software was used to quantify Lyve-1–positive, MECA32-negative regions in 66cl4-scramble and 66cl4-Six1 KD tumors. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.