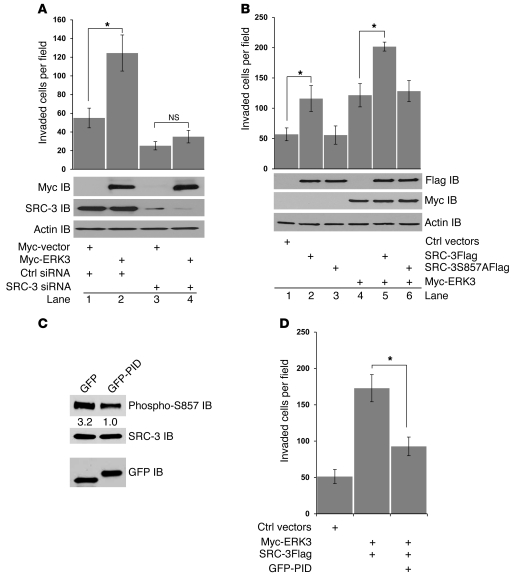
Figure 4. ERK3 promotes A549 cell invasion in a SRC-3–dependent manner, and S857 phosphorylation of SRC-3 is critical in promoting cell invasion.
(A) Transwell Matrigel cell invasion assay of A549 cells transiently transfected with Myc-ERK3 or the empty vector or together with either SRC-3 siRNA or nontargeting control siRNA. ERK3 overexpression and SRC-3 knockdown were demonstrated by Western blotting using a Myc Ab and a SRC-3 Ab, respectively. ERK3 lost the capability of promoting A549 cell invasion when SRC-3 was depleted. *P < 0.05. (B) Transwell Matrigel cell invasion assay of A549 cells transiently transfected with SRC-3Flag, SRC-3S857AFlag, or Myc-ERK3 or cotransfected with 2 of the constructs as indicated. Exogenous expression of SRC-3 and/or ERK3 was analyzed by Western blotting using a Flag Ab and a Myc Ab, respectively. Intact S857 is required for SRC-3 to promote cell invasion. (C and D) Inhibition of PAKs by expression of the PID greatly decreased the phosphorylation of SRC-3 at S857 and the effect of ERK3 and SRC-3 expression in cell invasion. GFP or GFP-PID fusion protein was overexpressed in A549 cells. (C) The effect of GFP-PID overexpression on the phosphorylation of SRC-3 at S857 was determined by Western blotting using an Ab that specifically recognizes phosphorylated S857. Numbers represent the relative intensity of the protein bands. The band intensity in the right lane is set as “1.0.” (D) The effect of GFP-PID overexpression on A549 cell invasion that was stimulated by ERK3 and SRC-3 was analyzed by transwell Matrigel cell invasion assay. *P < 0.01.