Figure 2.
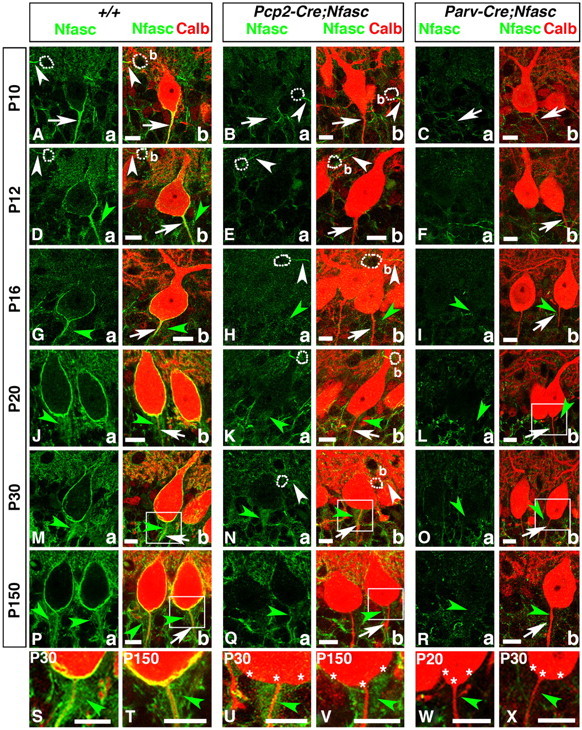
Purkinje and basket-specific ablation of Neurofascin reveals its localization to both Purkinje and basket neurons. Wild-type, Pcp2-Cre;NfascFlox and Parv-Cre;NfascFlox cerebellar sections from ages P10–P150 as indicated on left (A–R) or within panel (S–X), and immunostained against Nfasc (a, green) and Calb (b, red). Note that in P10 wild-type cerebella, Nfasc is localized to the Purkinje AIS (A, arrows) and basket (b) AIS (A, white arrowheads). At later stages, in wild-type cerebella, Nfasc is localized around the entire Purkinje soma and AIS (D, G, J, M, P, arrows), as well as the basket AIS (D, white arrowhead). Nfasc is also localized to basket axon terminals as they form the pinceau in wild-type cerebella (D, G, J, M, P, green arrowheads). In Pcp2-Cre;NfascFlox cerebella, Nfasc is ablated from the Purkinje soma/AIS (B, E, H, K, N, Q, arrows) but remains at the basket AIS (B, E, H, N, white arrowhead) and pinceau (H, K, N, Q, green, arrowheads). In Parv-Cre;NfascFlox cerebella, Nfasc is lost from the Purkinje soma/AIS (C, F, I, L, O, R, arrows), basket AIS, and pinceau (I, L, O, R, green arrowheads). Higher magnification shows that Nfasc is present at the Purkinje soma/AIS and pinceau in wild-type (S, T, green arrowheads), is missing from the Purkinje soma/AIS in Pcp2-Cre;NfascFlox (U, V, stars), while remaining at the pinceau in Pcp2-Cre;NfascFlox (U, V, green arrowheads), and is missing from both the Purkinje soma/AIS (stars) and the pinceau (green arrowheads) in Parv-Cre;NfascFlox cerebella (W, X). Scale bars: 10 μm.
