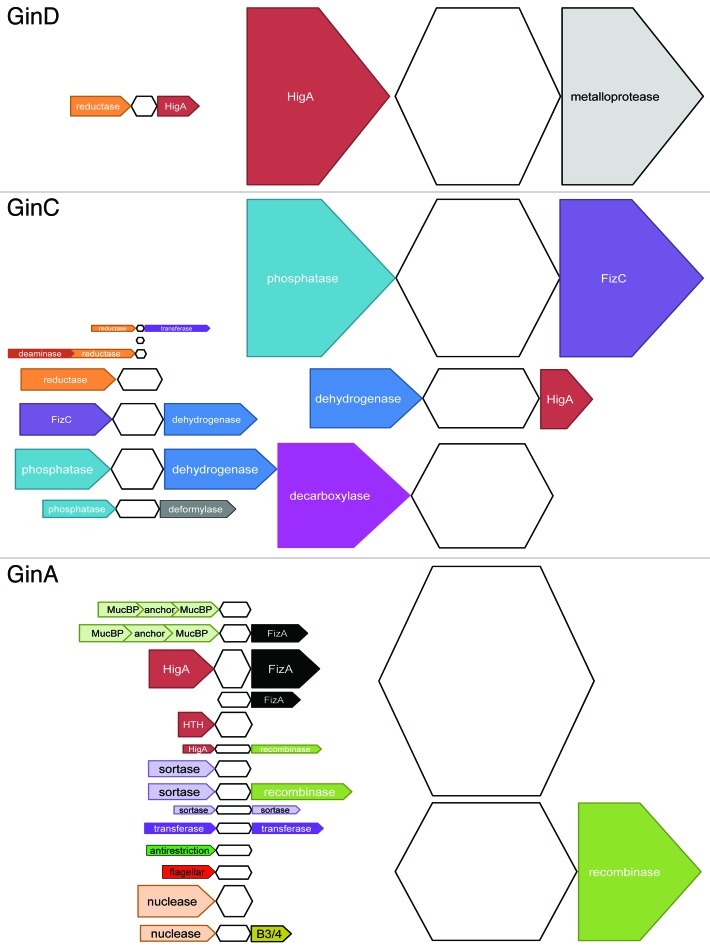
Figure 1. Genetic neighborhood of the GinA, GinC and GinD toxin super-families White shapes represent the toxins; colored shapes represent the flanking ORFs, and the conserved domains that have been identified and classified into larger categories. Flanking ORFs for which no conserved domain has been identified are not indicated. Length of ORFs is arbitrary. Height corresponds to the proportion of flanking ORFs within each toxin super-family. (A) Antitoxins associated with the GinD sequences. Twenty-five GinD sequences and their flanking ORFs have been detected among which five are not represented because they are under-represented. (B) Antitoxins associated with the GinC sequences. One-hundred-seventy-two GinC sequences and their flanking ORFs were detected among which 15 are not represented because they are under-represented. (C) Antitoxins associated with the GinA sequences. One-hundred-forty-seven GinA sequences and their flanking ORFs were detected among which 39 are not represented because they are under-represented.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.