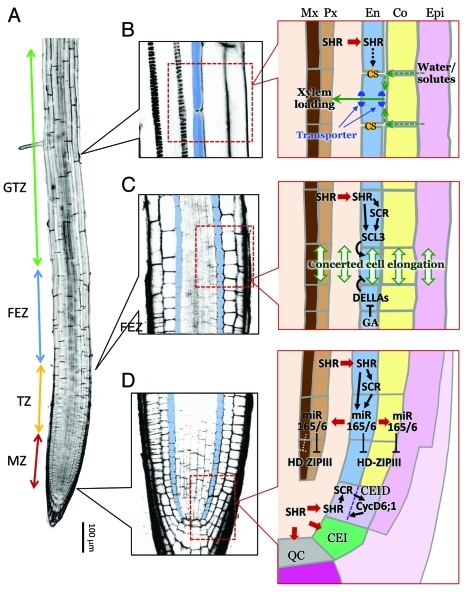
Figure 2.
Developmental zones of the Arabidopsis root and the signal transduction pathways and nutrient flow in the region of the root endodermis. (A) A confocal section of an Arabidopsis root. The four developmental zones, i.e., the meristematic zone (MZ), transition zone (TZ), fast elongation zone (FEZ), and growth terminating zone (GTZ) are labeled. (B-D) Magnified views of selected root regions (left; blue color indicates endodermis) and schematic representations of water/solute flow and developmental signaling in the endodermis (right). (B) Formation of the CS (represented as orange dots) and its role in regulating water and solute uptake. (C) GA- and SCL3-mediated control of endodermal cell elongation and its effect on the elongation of adjacent cell layers. (D) SHR- and miR165/6-mediated intercellular signaling between the endodermis and surrounding tissues. Arrows indicate activation/promotion, and T bars represent inhibition/suppression. Thick red arrows indicate cell-cell trafficking.