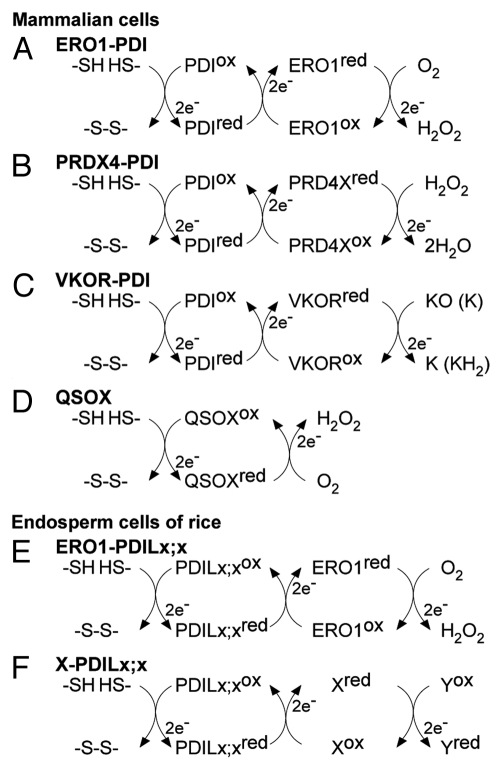
Figure 1.
Multiple electron transfer pathways for oxidative protein folding in the ER of mammalian and endosperm cells. Listed pathways are (A) ERO1-PDI, (B) peroxiredoxin IV (PRDX4)-PDI, (C) vitamin K epoxide reductase (VKOR)-PDI, and (D) quiescin sulfhydryl oxidase (QSOX), which all facilitate oxidative protein folding in the ER of mammalian cells. In the ER of rice endosperm, it is unlikely that OsERO1 directly oxidizes the active sites of OsPDIL1;1. Instead, it is plausible that OsERO1 oxidizes as-yet-unidentified members of the PDI family, indicated by PDILx;x, to promote the oxidative folding of storage proteins (E). Although there is no direct evidence, other oxidoreductases (X) and some members of the PDI family, indicated by PDILx;x, may also operate in oxidative folding of storage proteins (F). Yox represents unidentified electron acceptors, such as O2, H2O2, and quinone (F). KO, vitamin K epoxide; K, quinone; KH2, hydroquinone.