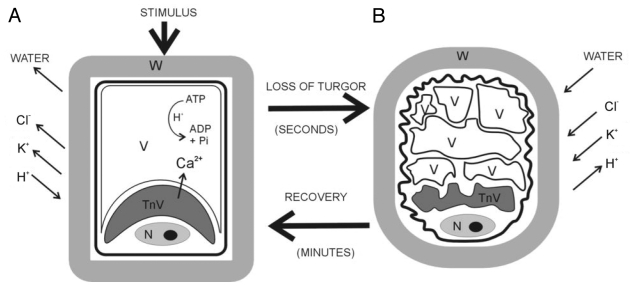
Figure 2.
Schematic representation of the variation in motor cell shape. The cell remains swollen if pulvini movement is inactive (A), whereas it becomes shrunken after pulvini response (B). Motor cells contain two vacuole types, one tannin-rich (TnV) located near the nucleus (N), the other aqueous and central (V). During shrinkage both vacuoles change their shape. K+ and Cl- fluxes mediate movement by triggering osmotic movement of water. In a cell gaining volume the energy-dependent pumping of protons out of the cell drives K+ uptake through specific inward-directed K+ channels. In a cell losing volume the flux of Cl- out of the cell down its concentration gradient drives K+ efflux through specific outward-directed K+ channels. The electrochemical gradient that enables rapid ion transport through plasma membranes is generated by H+-ATPase.