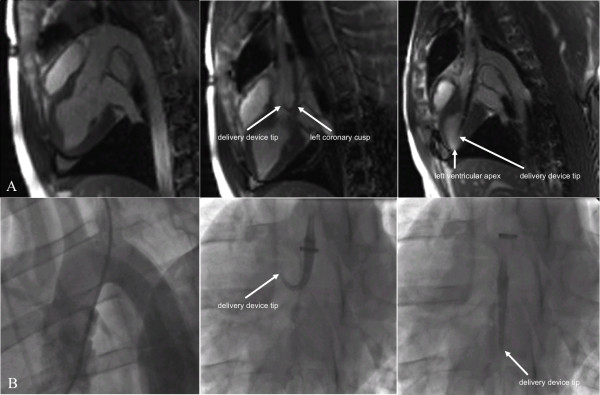
Figure 3.
Comparison of rtCMR (A) and fluoroscopic guidance (B) during aortic valve passage. rtCMR provides real-time anatomic orientation with excellent soft-tissue contrast (A, left image). Fluoroscopy lacks this detailed soft-tissue contrast and requires (repeated) injection of contrast media to obtain a reliable orientation of the surrounding anatomy (B, left image). Moreover, rtCMR offers clear determination of the position of the delivery device and, especially, the delivery device tip similar to fluoroscopy (A and B, middle and right images). Note the bending of the delivery device tip in the middle image. With rtCMR it can be clearly determined that the delivery device is stuck in the left coronary cusp of the aortic valve and needs to be retracted and advanced again for safe valve passage. Once the valve is passed, rtCMR allows for precise advancement of the delivery catheter until the device tip is located in the left ventricular apex (A, right image)