Abstract
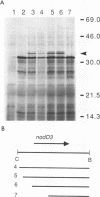
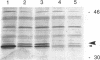
The nodulation (nod) genes of the symbiont Rhizobium meliloti are transcriptionally controlled by protein activators in the nodD gene family. While NodD1 and NodD2 act in concert with small molecular weight inducers provided by the host legume plant, NodD3 is an inducer-independent activator of the nod promoters. We determined the sequence of the nodD3 gene, confirmed the expression of a 35 kDa protein in vitro, and determined the insertion points of five Tn5 insertions in the region of the nodD3 gene. We found the NodD3 amino acid sequence to be markedly diverged from the sequences of NodD1 and NodD2, which were more similar to the inducer-dependent NodD of another species, Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar viciae. The expression of nodD3 is not well understood, but involves at least SyrM, another positive activator related to the LysR-NodD family. One of the phenotypically mutant Tn5 insertions used in genetic studies of NodD3-dependent nod regulation lacks NodD3 protein as determined by Western blots, but another expresses about 50-60% of the wild type level. The location of these Tn5 insertions substantially upstream of the open reading frame for NodD3 suggests importance of relatively distant regulatory sequences for nodD3 expression. An insertion that did not cause a NodD3- phenotype is located in the extreme C-terminus of the protein coding region.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnett M. J., Long S. R. DNA sequence and translational product of a new nodulation-regulatory locus: syrM has sequence similarity to NodD proteins. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):3695–3700. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.3695-3700.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beringer J. E. R factor transfer in Rhizobium leguminosarum. J Gen Microbiol. 1974 Sep;84(1):188–198. doi: 10.1099/00221287-84-1-188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burn J. E., Hamilton W. D., Wootton J. C., Johnston A. W. Single and multiple mutations affecting properties of the regulatory gene nodD of Rhizobium. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1567–1577. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00142.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis E. O., Johnston A. W. Analysis of three nodD genes in Rhizobium leguminosarum biovar phaseoli; nodD1 is preceded by noIE, a gene whose product is secreted from the cytoplasm. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jun;4(6):921–932. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00665.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelhoff T. T., Fisher R. F., Jacobs T. W., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Nucleotide sequence of Rhizobium meliloti 1021 nodulation genes: nodD is read divergently from nodABC. DNA. 1985 Jun;4(3):241–248. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egelhoff T. T., Long S. R. Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes: identification of nodDABC gene products, purification of nodA protein, and expression of nodA in Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):591–599. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.591-599.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faucher C., Maillet F., Vasse J., Rosenberg C., van Brussel A. A., Truchet G., Dénarié J. Rhizobium meliloti host range nodH gene determines production of an alfalfa-specific extracellular signal. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5489–5499. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5489-5499.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Egelhoff T. T., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Specific binding of proteins from Rhizobium meliloti cell-free extracts containing NodD to DNA sequences upstream of inducible nodulation genes. Genes Dev. 1988 Mar;2(3):282–293. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.3.282. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Long S. R. DNA footprint analysis of the transcriptional activator proteins NodD1 and NodD3 on inducible nod gene promoters. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5492–5502. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5492-5502.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher R. F., Swanson J. A., Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Extended Region of Nodulation Genes in Rhizobium meliloti 1021. II. Nucleotide Sequence, Transcription Start Sites and Protein Products. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):191–201. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Haughn G. W., Calvo J. M., Wallace J. C. A large family of bacterial activator proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6602–6606. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honma M. A., Asomaning M., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti nodD genes mediate host-specific activation of nodABC. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):901–911. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.901-911.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honma M. A., Ausubel F. M. Rhizobium meliloti has three functional copies of the nodD symbiotic regulatory gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8558–8562. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvath B., Bachem C. W., Schell J., Kondorosi A. Host-specific regulation of nodulation genes in Rhizobium is mediated by a plant-signal, interacting with the nodD gene product. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):841–848. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04829.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs T. W., Egelhoff T. T., Long S. R. Physical and genetic map of a Rhizobium meliloti nodulation gene region and nucleotide sequence of nodC. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):469–476. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.469-476.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium genetics. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:483–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIver J., Djordjevic M. A., Weinman J. J., Bender G. L., Rolfe B. G. Extension of host range of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. trifolii caused by point mutations in nodD that result in alterations in regulatory function and recognition of inducer molecules. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1989 May-Jun;2(3):97–106. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-2-097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Long S. R., Ruvkun G. B., Brown S. E., Ausubel F. M. Physical and genetic characterization of symbiotic and auxotrophic mutants of Rhizobium meliloti induced by transposon Tn5 mutagenesis. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.114-122.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. A family of activator genes regulates expression of Rhizobium meliloti nodulation genes. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):7–18. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan J. T., Long S. R. Induction of Rhizobium meliloti nodC expression by plant exudate requires nodD. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6609–6613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R., Lipman D. J. Improved tools for biological sequence comparison. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2444–2448. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2444. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rostas K., Kondorosi E., Horvath B., Simoncsits A., Kondorosi A. Conservation of extended promoter regions of nodulation genes in Rhizobium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1757–1761. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma S. B., Signer E. R. Temporal and spatial regulation of the symbiotic genes of Rhizobium meliloti in planta revealed by transposon Tn5-gusA. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):344–356. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.344. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subbiah S., Harrison S. C. A method for multiple sequence alignment with gaps. J Mol Biol. 1989 Oct 20;209(4):539–548. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90592-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J. A., Tu J. K., Ogawa J., Sanga R., Fisher R. F., Long S. R. Extended Region of Nodulation Genes in Rhizobium meliloti 1021. I. Phenotypes of Tn5 Insertion Mutants. Genetics. 1987 Oct;117(2):181–189. doi: 10.1093/genetics/117.2.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tautz D., Renz M. An optimized freeze-squeeze method for the recovery of DNA fragments from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):14–19. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90419-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. M., Weber D. K., Johnson T., Sakaguchi A. Y. Supercoil sequencing using unpurified templates produced by rapid boiling. Biotechniques. 1988 Oct;6(9):839, 841-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]