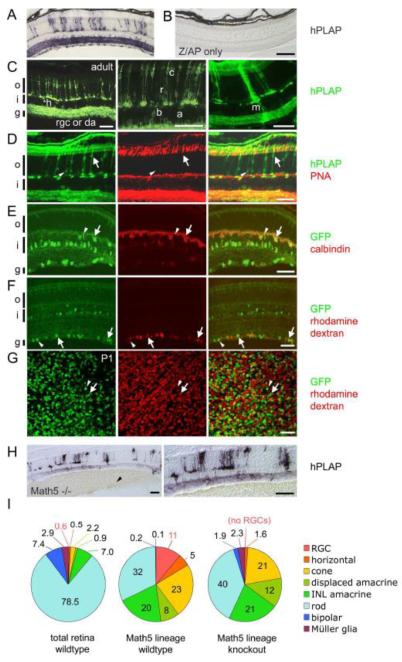
Fig. 3.
Math5+ progenitors contribute differentially to all retinal cell types. Math5>Cre mice were crossed to Z/AP (A-D) or R26floxGFP reporter (E-G) strains. (A) In Math5>Cre; Z/AP mice, hPLAP+ descendants of Math5+ progenitors represent 3% of adult retinal cells (see Table 1) and are present in every cell layer. (B) Z/AP-only control retinas have no hPLAP activity. (C) Math5+ descendants, detected by hPLAP immunostaining, include horizontal (h), ganglion (rgc), displaced amacrine (da), INL amacrine (a), bipolar (b), rod (r), cone (c) and Müller glial (m) cells. (D) Math5+ cone (arrows) and rod (arrowheads) photoreceptors are distinguished by co-labeling with anti-hPLAP and cone-specific PNA lectin. Non-specific labeling of pigment epithelium and choroid reflects mouse IgG crossreactivity. (E-G) In Math5>Cre; R26floxGFP mice, Math5+ horizontal cells (E, arrows) are marked by GFP and calbindin immunoreactivity. The arrowhead shows a solitary Math5+ bipolar cell. (F-G) Math5+ RGCs (arrows) and displaced amacrines (arrowheads) in the GCL are shown in adult retinal sections (F) or P1 retinal flatmounts (G). RGCs are distinguished by retrograde labeling of optic nerve axons with rhodamine dextran. There is no difference in the GFP+ fraction of rhodamine dextran-labeled RGCs between these two ages. (H) The fate of Math5>Cre-expressing progenitors in Math5 −/− mice. hPLAP+ cells are distributed throughout the retina, but RGCs are lacking. Vitreal hemorrhages (arrowhead) are common in Math5−/− mice. (I) The distribution of cell fates in the entire retina (from Jeon et al., 1998), in the Math5 lineage of wild-type mice, and in the Math5 lineage of knockout mice. The Math5 lineage is biased toward early-born cell types (RGC, horizontal, cone), although rods are the most common fate adopted by Math5+ cells. In the Math5 knockout, lineage-derived cells adopt all retinal fates except for RGCs. hPLAP, human placental alkaline phosphatase; o, outer nuclear layer; i, inner nuclear layer; g, ganglion cell layer. Scale bars, 100 m in A-B, H; 50 m in C-G.