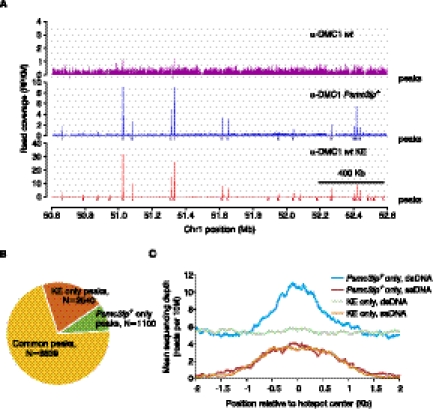
Figure 5.
Mapping meiotic DSB hotspots in wt mice using SSDS. (A) Meiotic DSB maps obtained using wt mice and regular ChIP-seq (α-DMC1 wt), Psmc3ip−/− mice, and regular ChIP-seq (α-DMC1 Psmc3ip−/−, reference data set; Smagulova et al. 2011) or using wt mice and SSDS (α-DMC1 wt KE) in a 2 Mb region of chromosome 1. We plot read coverage for all reads without ssDNA identification for regular ChIP-seq samples. Although peaks are located at the same places, hotspot detection is more sensitive in the KE library because of the lower background. Peaks are virtually undetectable in the wt sample prepared without kinetic enrichment. (B) Most hotspots are shared between the reference Psmc3ip−/− data set and the wt KE samples. We detected hotspots in the α-DMC1 wt KE sample and compared their positions with the published hotspots (Smagulova et al. 2011). The number of peaks shared by and unique to these two data sets are plotted. (C) Hotspot detection in the wt KE sample is more specific. Mean depth of ssDNA and dsDNA read coverage (reads per 10 million reads) of Psmc3ip−/− only (reference set) and KE only hotspots.