Figure 4.
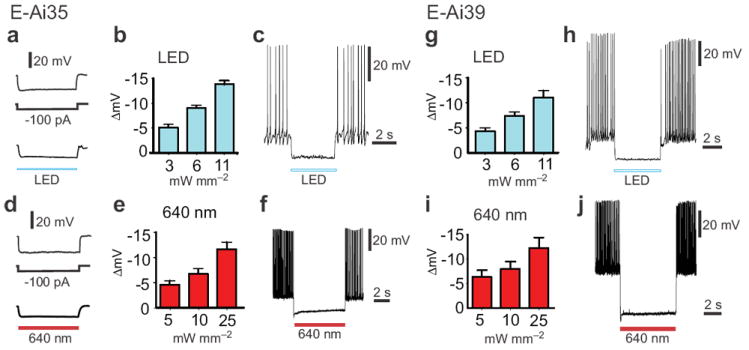
Alternative light sources for silencing of cortical pyramidal neurons in Emx1-Cre;Ai35 (E-Ai35) and Emx1-Cre;Ai39 (E-Ai39) mice. (a-c) Inhibition of E-Ai35 neurons by a white LED. (a) An example E-Ai35 neuron exhibited similar hyperpolarization response to negative current injection (-100 pA) and illumination by white light. (b) White light dose-response curve (n = 3). (c) An example of effective silencing by white light (11 mW mm-2) of APs evoked by a positive current injection (+100 pA). (d-f) Inhibition of E-Ai35 neurons by red laser light (640 nm). (d) An example E-Ai35 neuron exhibited similar hyperpolarization response to negative current injection (-100 pA) and illumination by red light. (e) Red light dose-response curve (n = 7). At the highest tested intensity (25 mW mm-2) the 640-nm laser illumination achieved 43% ± 5% of the hyperpolarization achieved with the 593-nm laser. (f) An example of silencing of current-evoked APs by red laser light. (g-h) Inhibition of E-Ai39 neurons by a white LED. (g) White light dose-response curve (n = 5). (h) An example of silencing of current-evoked APs by white light. (i-j) Inhibition of E-Ai39 neurons by red laser light (640 nm). (i) Red light dose-response curve (n = 7). At the highest tested intensity (25 mW mm-2) the 640-nm laser illumination achieved 100% ± 35% of the hyperpolarization achieved with the 593-nm laser. (j) An example of silencing of current-evoked APs by red laser light.
