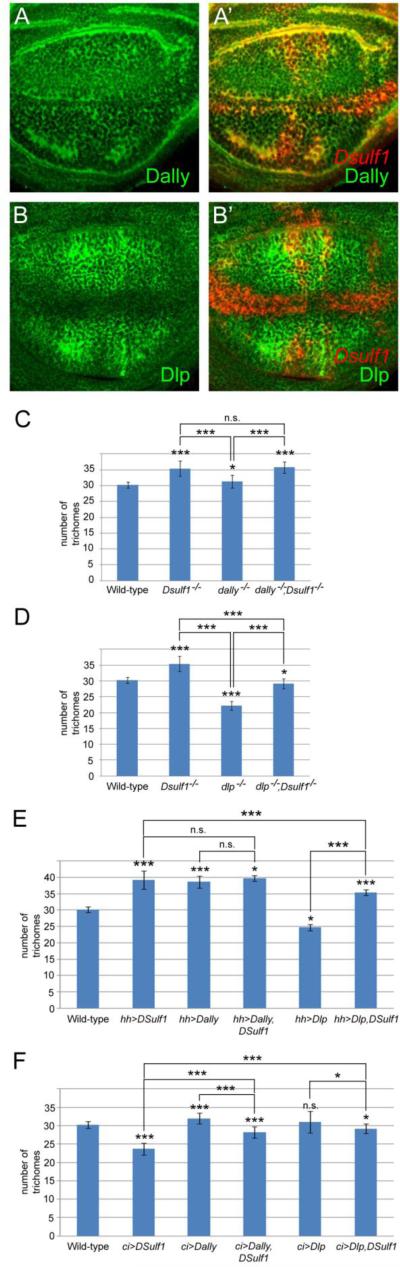
Figure 8. Genetic interactions between Dsulf1, dally and dlp.
(A-B) Immunodetection of Dally (A) and Dlp (B) in wt late 3rd instar wing discs. (A’-B’) Double detections of Dsulf1 (red) and Dally (green, A’) or Dlp (green, B’) show that Dsulf1 expression overlaps with both Dally and Dlp except at the margin where Dlp is not detected. (C-F) Phenotypic analysis of adult wings by quantifying the number of trichomes between L3 and L4 veins, at the level of the posterior crossvein. (C-D) Comparison of Dsulf1 (Dsulf1-/-), dally (dally-/-, C) or dlp (dlp-/-, D) simple mutants with dally/Dsulf1 (dally-/-;Dsulf1-/-, C) and dlp/Dsulf1 (dlp-/-;Dsulf1-/-,D) double mutant adult wings. (E-F) Over-expression of Dsulf1, dally or dlp alone or in combination in the P compartment using a hh-Gal4 driver (E) or in the A compartment using a ci-Gal4 driver (F). Results are expressed as the mean number of trichomes ± standard deviation. Statistical significance compared to wt is indicated on top of each bar. Other comparisons are marked by horizontal bars, and statistical significance is indicated (***=P<0.0005, *=P<0.05, n.s. for non significant difference).