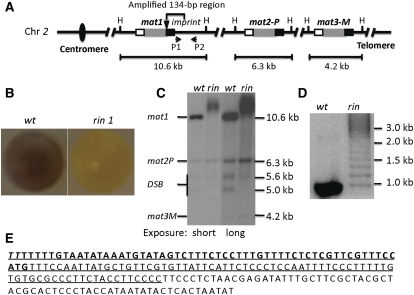
Figure 1 .
Broadly diffused mat1-DNA bands of the rin1 mutant. (A) Mating-type loci. The three mating-type cassettes are indicated. The internal P (1104-bp-long DNA sequence) and M (1128-bp) allele-specific sequences are shown in shaded boxes; the flanking homology boxes H2 (135 bp) and H1 (59 bp) are shown in open and solid boxes, respectively; the solid triangle represents the imprint site; H indicates the HindIII site. The sizes of three mat cassette-containing fragments generated by HindIII digestion of genomic DNA are indicated. A is not drawn to scale. (B) Iodine-vapor-stained colonies of the wild type (wt; strain SP976) and the rin1 mutant (SP2579). (C) Southern blot analysis of the wild type (SP2533) and the rin1 mutant (SP2579) using standard DNA extraction and Southern blot methods (Moreno et al. 1991). The blot was probed with a mat1P-containing, HindIII 10.6-kb fragment. This probe also detected mat2 and mat3 bands due to the shared homology between cassettes defined in A. To depict low-intensity bands, the same blot was exposed to X-ray film for 1 hr (short exposure) or for 5 hr (long exposure). (D) PCR analysis of mat1-distal sequences. The location of primers P1 (ATTCATTCTCCCTCCAATTTTCCC) and P2 (GGAGATAGGAGTGTGATTGAAGGTG) is shown in A. The PCR reactions were performed according to the vendor’s protocol (Clonetaq Titanium Taq, catalog no. 639210). The PCR products were separated on 3% agarose gel and stained with ethidium bromide before taking the picture. (E) The amplified sequence of the rin1 mutant. The sequence shows a 200-bp region, which includes the 59-bp H1 (boldface type) and the H1-distal sequence. The 134-bp sequence amplified in the rin1 mutant is underlined. The italicized TT bases located at the 5′ end of the sequence indicate the imprint site. The genotype of strain is listed in Table S1.