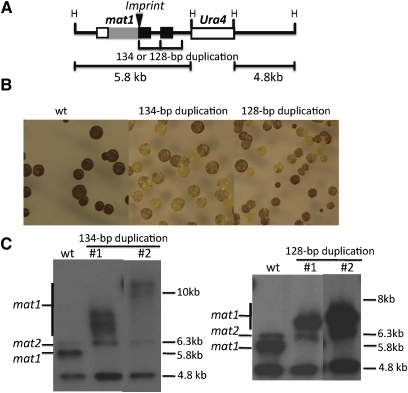
Figure 2 .
Generation of new rin alleles. (A) Schematic structure of genetically engineered rin alleles. A 134- or 128-bp duplicated sequence, together with the 1.8-kb ura4+-containing HindIII fragment, was placed into the mat1 locus using the standard lithium acetate transformation procedure by selecting for the ura4+ marker (Moreno et al. 1991). The symbols are those as defined Figure 1A. (B) Iodine-staining phenotype of new rin mutants. The wild-type CY83 control strain contained only the ura4+ mark insertion, and in addition, the CY96 and CY84 strains contained the 134- and the 128-bp duplication, respectively. (C) Southern blot analyses of HindIII-digested genomic DNA of engineered rin derivatives. Two independent, very-light-iodine-staining colonies derived from strains CY96 or CY84 were analyzed along with the CY83 control. The probe used was as described in Figure 1C.