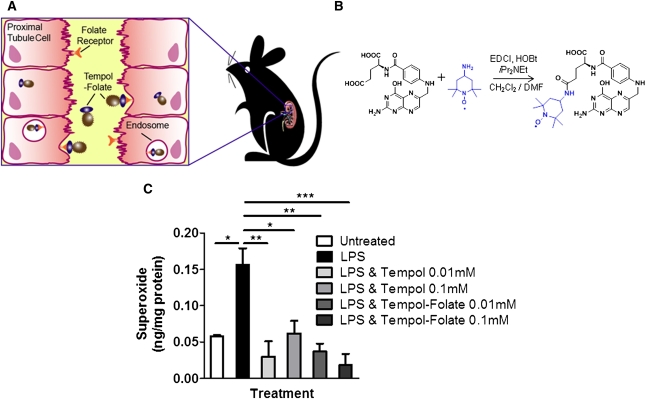
Figure 1.
Conjugation of folic acid to the antioxidant tempol selectively targets the proximal tubule cells (HK-2) that express high levels of folate receptor, without altering its ability to scavenge superoxide. (A) Schematic showing how tempol-folate conjugate binds to tubule folate receptors on the epithelium-like layer of the proximal tubule cells, is taken up into endosomes, and released into the cell. (B) Structure and synthesis of tempol-folate conjugate. Tempol-folate can be readily synthesized from folic acid and 4-amino tempol via EDC coupling. (C) Superoxide concentration in cultured HK-2 cells treated with 0.1 μg/ml LPS endotoxin with or without 0.01–0.1 mM tempol or tempol-folate, measured by DHE-HPLC (n=3). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001 comparing the LPS-treated group with all other groups. Superoxide concentration was normalized to protein concentration.