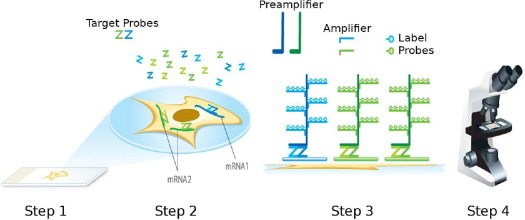
Figure 1.
Schematic of the RNAscope assay procedure. In step 1, cells or tissues are fixed and permeabilized to allow for target probe access. In step 2, target RNA-specific oligonucleotide probes (Z) are hybridized in pairs (ZZ) to multiple RNA targets. In step 3, multiple signal amplification molecules are hybridized, each recognizing a specific target probe, and each unique label probe is conjugated to a different fluorophore or enzyme. In step 4, signals are detected using an epifluorescent microscope (for fluorescent label) or standard bright-field microscope (for enzyme label).