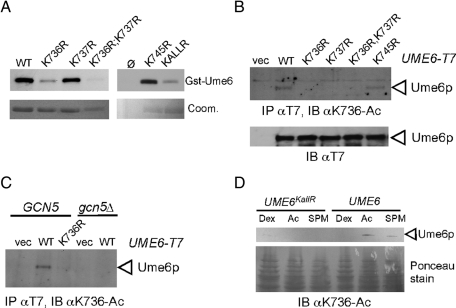
FIGURE 2:
In vivo Ume6p acetylation requires Gcn5p. (A) In vitro acetylation assays described in Figure 1 were repeated with the indicated Gst-Ume6 substitution mutants as substrate. Gels were Coomassie stained (Coom.) before fluorography and used to control for substrate addition. (B) Extracts prepared from log-phase RSY10 cultures expressing the indicated GAL-T7-UME6 alleles (or the vector control) were blotted and probed with α-K736-Ac antibodies. (C) The experiment described in B was repeated in the wild-type (RSY10) and gcn5∆ mutant (RSY622) strains. (D) Endogenous Ume6p (RSY1079) or Ume6pKallR (RSY1149) was detected in extracts derived from mid-log cultures growing in dextrose, acetate, or after the switch from acetate to SPM. K736 acetylation was monitored by Western blot analysis probing with α-K736-Ac. Ponceau staining of the gel is shown as loading control.