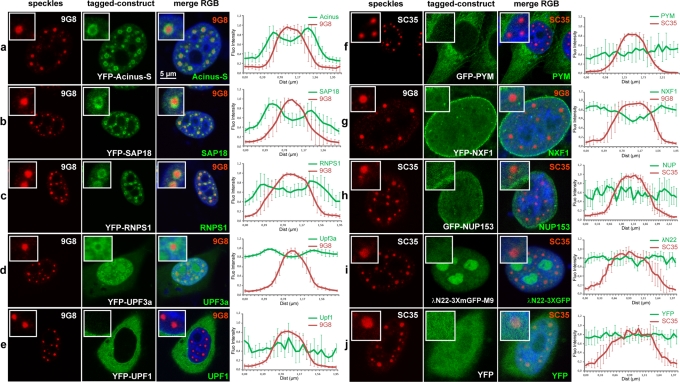
FIGURE 2:
A subset of nuclear peripheral EJC factors accumulates in perispeckles. HeLa cells were transfected with various constructs encoding fluorescence-tagged fusion proteins (green) and colabeled with the endogenous SR protein 9G8 (a–e, g) or SC35 (f, h–j; red). Peripheral EJC factors that are known to associate either in the nucleus (Acinus-S, SAP18, RNPS1, Upf3a, NXF1) or in the cytoplasm (Upf1, PYM) were analyzed. Different constructs were also used as negative controls and include the YFP protein alone, the nucleoporin NUP153, and the reporter gene λN22-3XmGFP-M9, which is specifically targeted to nucleoli. Nuclei were counterstained using the Hoechst-33258 dye (blue). Insets are centered on a representative speckle and show 3× (b–e, i), 2.5× (a, f, h, j), and 2× (g) magnifications. Right, mean fluorescence intensity line scans of the images, using line sections on five selected speckles, as described. The factors constituting the ASAP complex, Acinus-S, RNPS1, and SAP18 proteins, are enriched in perispeckles (a–c), as well as in the NMD factor Upf3a, which is partially enriched in this area (d). In contrast, the cytoplasmic NMD factor Upf1 and the EJC disassembly protein PYM are mainly in the cytoplasmic compartment (e, f). Finally, the nuclear export factor TAP (NXF1) is both diffuse in the nucleoplasm and associated with the nuclear envelope (g). Scale bar, 5 μm.