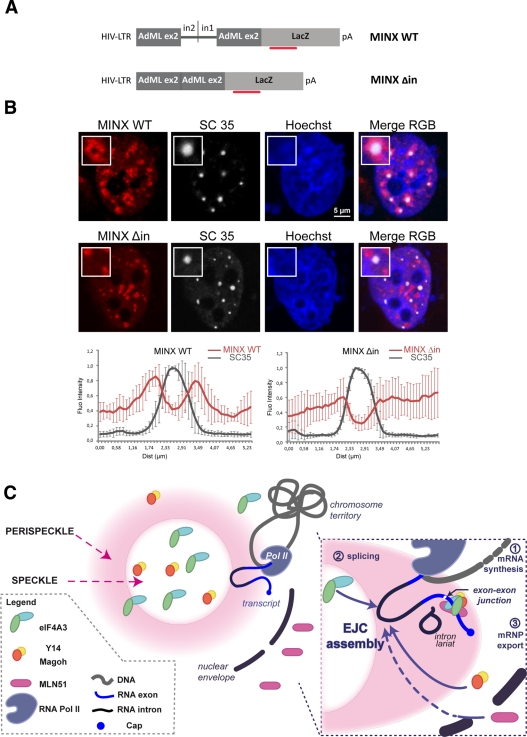
FIGURE 8:
Intron-containing RNAs concentrate around nuclear speckles. (A) Scheme of the MINX constructs. The plasmid comprises the LTR-HIV promoter, followed by the MINX sequence fused to the LacZ coding sequence. The MINX sequence consists of adenovirus major late gene sequences (AdML): an exon2/intron2 sequence fragment is fused to a fragment of intron1/exon2 sequence (MINX WT). For MINX Δin, the fused intron2/intron1 is excised. The red bar represents the position of the FISH probes. (B) MINX WT is recruited at the periphery of nuclear speckles. HeLa cells were cotransfected with either MINX WT or MINX Δin and Tat-expressing vector. Cells were then processed for combined immunofluorescence LacZ FISH. A pool of fluorescent Cy3-LacZ probes was hybridized for MINX reporter detection (red). The endogenous SC35 protein was stained with anti-SC35 (white) antibody. Nuclei were counterstained with the Hoechst-33258 dye (blue). Insets show a representative speckle with a 2.5× magnification. Line-scan graphs were analyzed as previously mentioned. Scale bar, 5 μm. (C) Model for the assembly of the EJC core. Unassembled Magoh/Y14 and eIF4A3 are in the nucleus, whereas MLN51 is in the cytoplasm. Nascent pre-mRNAs exiting from Pol II (step1) are processed into mRNP (step2) in perispeckles. Following spliceosome assembly, eIF4A3 and Magoh/Y14 are recruited onto the RNA. After splicing completion, MLN51 joins the complex. The stable EJC core recruits peripheral factors (step 3).