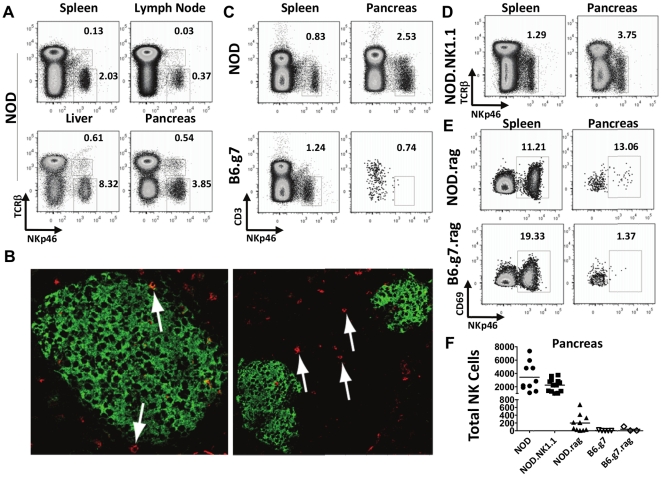
Figure 1. NK cells reside in the pancreas.
A) Flow cytometric analysis of leukocytes isolated from enzyme-digested tissues of NOD mice. Plots are of CD45+ cells and numbers are percentages of CD45+ cells. Example of one of six similar experiments. B) Using immunohistochemistry, NK cells (red) were found in the surrounding peri-islet infiltrates (left panel 40×) and in infiltrated islets (right panel 20×). Insulin was stained green to define islets. Example of sections of pancreas from three different NOD mice, evaluating a minimum of 10 slides per mouse. C) NK cells were more numerous in NOD pancreas compared to B6.g7 pancreas– dots were enlarged to allow visualization of NK cells due to low number of events obtained from B6.g7 mice. D) NOD.NK1.1 pancreata contain similar frequencies of NK cells as NOD mice. E) Rag2−/− NOD mice have low numbers of NK cells in their pancreas, whereas Rag1−/− B6.g7 mice have very few, almost undetectable numbers of NK cells in the pancreas. F) Absolute numbers of NK cells recovered from the pancreas of individual mice from noted strains. Example from one of six similar experiments, each with a minimum of three mice per strain is shown.