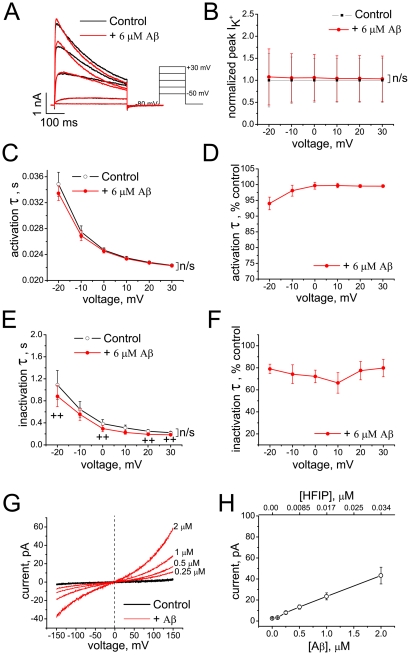
Figure 5. Effects of Aβ1–42 oligomers (HFIP protocol II) on Kv 1.3 currents and on BLM conductance.
(A) Representative K+ currents evoked by depolarizing voltage steps from the holding potential of −80 mV before (black) and after (red) application of Aβ1–42 oligomers. (B) Peak K+ currents normalized to mean control values at different voltages after application of Aβ1–42 oligomers. The differences in peak current amplitude before and after application of Aβ are not significant (F = 3.9; P = 0.08 two-way RM-ANOVA). (C–F) Activation and inactivation kinetics of K+ currents before (black) and after application of Aβ1–42 oligomers (red) shown in absolute (C, E) and normalized (D, F) values of time constants at different voltages (mean ± S.E.M., n = 4 cells). The effect of Aβ on the activation time constant was not significant in Tests of Within-Subjects Effects (F = 4.4; #P = 0.07, Two-way RM-ANOVA). ANOVA analysis also revealed no significant effect of Aβ on the inactivation time constant (F = 8.7; #P = 0.05, Two-way RM-ANOVA), however two-way paired t-Test, (++P<0.05) showed significant differences between mean time constant measured before and after treatment with Aβ, revealing the trend. (G) Representative I/V curves recorded on DOPC/DOPE BLMs before (black) and after (red) application of Aβ1–42 oligomers. (H) Dose-dependence of Aβ-induced currents at +150 mV across BLMs (mean ± S.E.M., n = 7 experiments, out of a total of 9, in which the effect was observed).