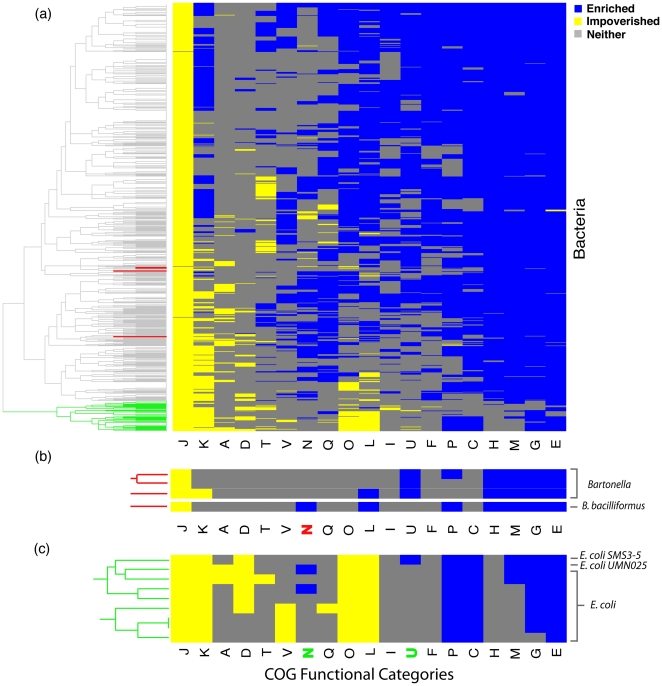
Figure 2. Visualizing high-level patterns of functional divergence.
We used hierarchical clustering to reveal the main patterns of functional divergence in our dataset of 750 bacterial proteomes. (a) The complete heatmap, with a dendrogram corresponding to category clustering, and species clustering along the left hand side. Visualizing the data in this way reveals the extreme impoverishment of proteins involved in ribosome biogenesis (J), as well as the enrichment of categories involved in interaction with the environment (E, M, G, H, C, P) across all species. (b) Lineage-specific events of functional divergence picked out from the heatmap (dendrogram colors denote the regions expanded upon – a larger version of the complete heatmap is available as Figure S1). Unlike other Bartonella species, B. bacilliformus is impoverished for divergence in cell motility genes (N), and is unique among Bartonella species in using a flagellum to infect erythrocytes. (c) Two strains of E. coli – SMS 3–5 and UMN026 – have phylogenetically atypical patterns of functional divergence: the constraints on cell motility (N) are among those that have relaxed relative to the other strains in SMS 3–5, while UMN026 is uniquely enriched for secretion system (U) genes.