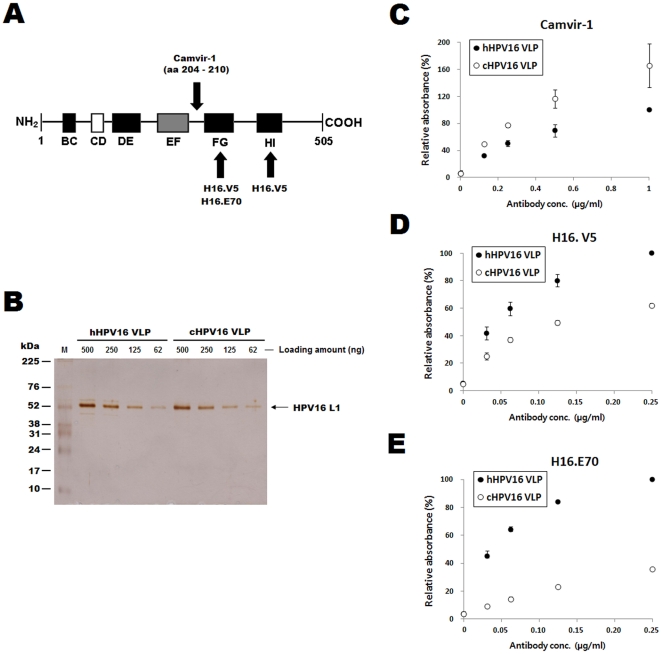
Figure 1. Camvir-1, H16.V5 and H16.E70 reactivity towards hHPV16 VLPs and cHPV16 VLPs.
The HPV16 L1 protein residues recognized by H16.V5, H16.E70 and Camvir-1 are displayed graphically in (A). BC, CD, DE, EF, FG and HI indicate the loop structures in HPV16 L1. The numbers refer to the amino acid residues as counted from the N-terminus, the black boxes indicate loops covering the solvent-exposed face of the capsid, and the white box (CD) indicates an internal loop. The gray box (EF) indicates a loop partly located on the outside of the capsid. The hHPV16 VLP and cHPV16 VLP concentrations were confirmed by SDS-PAGE prior to running ELISAs (B). The protein concentration of each VLP preparation was determined by Bradford protein assay, and 500 to 62 ng of proteins were loaded for SDS-PAGE analysis. M indicates the molecular weight marker. Camvir-1, H16.V5 and H16.E70 reactivity towards hHPV16 VLPs and cHPV16 VLPs was determined by direct ELISA. The ELISA results are presented in C, D and E, respectively. The ODs of the hHPV16 VLPs after reaction with 1 µg/ml of Camvir-1, 0.25 µg/ml of H16.V5 and 0.25 µg/ml of H16.E70 were set at 100% in C, D and E, respectively. The ELISA values are the means ± SD of two independent assays.