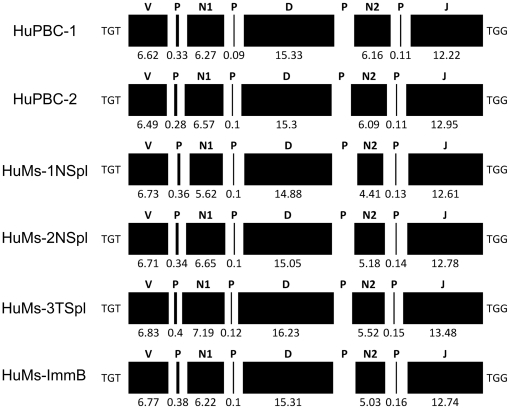
Figure 5. DNA deconstruction reveals IgM CDR-H3 repertoires that are normally diversified and indistinguishable between humanized NOD-scid-IL2Rγnull mice and normal human B cells.
The germline contribution of IGHV, IGHD, and IGHJ elements is illustrated. Shown are IgM CDR-H3 sequences containing an identifiable IGHD segment located between the IGHV conserved cysteine codon (TGT) and the conserved tryptophan codon (TGG) encoded by IGHJ elements. All components are shown to scale. Data comprises functional IgM sequences derived from unique CDR-H3s isolated from HuPBC-1, HuPBC-2, HuMs-1NSpl, HuMs-2NSpl, HuMs-3TSpl, and HuMs-ImmB using a previously published algorithm [24]. Preservation of IGHV, IGHD, and IGHJ germline sequences were statistically similar across all samples (Student’s t test). The degree of nontemplated N-region [N] additions, palindromic [P] nucleotide additions, and total CDR-H3 length were also statistically indistinguishable, except for a subtle increase in 3′ N-region addition among HuPBC (P = 0.03).