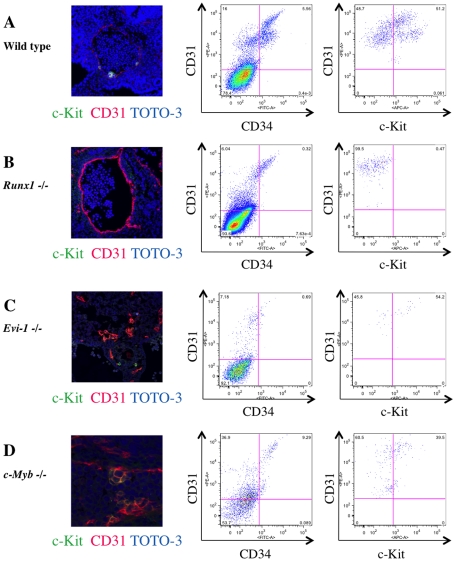
Figure 5. Altered IAC phenotype in Runx1-/-, Evi-1-/- and c-Myb-/- embryos.
Transverse sections of the AGM region were made from ICR, Runx1-/-, Evi-1-/- and c-Myb-/- mouse embryos at 10.5 dpc, stained with antibodies and observed by confocal microscopy. Single cell suspensions of AGM regions from these embryos at 10.5 dpc were prepared and analyzed by flow cytometry. (A-D) Left panels show confocal images stained with anti-c-Kit (green) and CD31 (red) antibodies and TOTO-3 (blue). Middle and right panels show flow cytometric profiles of CD34 (x-axis) and CD31 (y-axis), and c-Kit (x-axis) and CD31 (y-axis), respectively. Isotype control and compensation samples of flow cytometric analysis are shown in Figure S2 and S5. (A) ICR mouse embryos serve as (wild type) controls. IACs and CD31+/CD34+/c-Kit+ AGM cells were observed. (B) No IACs were observed in Runx1-/- embryos, whereas the aortic structure was conserved (left). No CD31+/CD34+/c-Kit+ AGM cells were observed, whereas CD31+/CD34+/c-Kit- AGM cells, which are equivalent to ECs, were observed (middle and right). (C) No IACs were observed and aortic structure was altered in Evi-1-/- embryos (left). CD31+ AGM cells were observed, but they did not express CD34 and c-Kit (middle and right). (D) IACs were observed in c-Myb-/- embryos and the aortic structure was conserved (left). CD31+/CD34+/c-Kit+ AGM cells were observed (middle and right).